Lithium battery applications are ubiquitous, but they require good management to ensure safe and reliable use, especially to prevent the voltage from dropping below the safety line, which we call over-discharge. This requires all batteries to have a safety protection function, which is low voltage cut-off protection, abbreviated as LVC.
It is like a smart safety switch. Its function is to automatically detect when the battery voltage is about to drop to a dangerous level and cut off the power supply from the battery to the device in time. This article will take you to explore how LVC works, why it is dangerous to ignore it, and the specific LVC values of different batteries.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat are the consequences of over-discharging lithium batteries

Each lithium battery has a safe voltage lower limit, just like the safety warning water level of a reservoir. Once the battery is discharged and the voltage is lower than this safety line, it will cause the battery to be over-discharged. The following are the specific hazards of over-discharge.
Permanent damage to battery performance. The available capacity of the battery will decrease. It can store 100Khw of electricity, but in reality it can only store 70~80Kwh of electricity. The internal resistance will increase, and the voltage will drop faster when discharging with large current, and the efficiency will decrease. The overall life will be greatly shortened. In theory, it can work for 5 years, but it will retire 2 years early.
It will cause safety hazards. Over-discharge will destroy the chemical structure inside the battery, which can easily cause a tiny short circuit inside the battery. If your battery has been severely over-discharged, it is very easy for it to heat up and bulge inside, and even thermal runaway.
In addition, although it is mainly to protect the battery, low voltage may also cause your connected devices to work improperly or even cause the device to fail to start.
What is low voltage cutoff (LVC)
LVC is an automatic protection switch, and its core task is to monitor the battery voltage in real time. Once it detects that the battery voltage is about to drop to the preset minimum safe voltage value, it will automatically disconnect the connection between the battery and the load.
Generally, they are protected by a protection board, BMS or PMC. One of the core functions is to implement LVC and protect the battery cells from over-discharge. There are also LVCs integrated into the equipment, such as common model aircraft drones. Another type is an independent LVC independent module.
Why LVC is critical to safety
It is designed to prevent over-discharge at the source, just like installing flood warning and gate control on the reservoir, never allowing the water level to fall below the warning value.
It greatly reduces the risk of thermal runaway. Overdischarge itself and the subsequent charging of overdischarged batteries may cause internal short circuits, heating, bulging, and even the most terrible thermal runaway (smoke, fire). LVC directly cuts off this potential dangerous fuse by preventing overdischarge.
With LVC, you can avoid premature failure of lithium ion batteries due to preventable reasons, allowing your battery to safely use its full design life.
Ensure the reliable operation of the entire system and equipment. If the battery voltage is too low, not only the battery itself is at risk, but the connected devices may also not work properly, such as lights flickering, controllers restarting, appliances failing to start, etc.
Therefore, LVC is not just a nice-to-have feature, it is the cornerstone of safe, long-lived and reliable operation of lithium batteries. It is directly related to personal and property safety, your equipment investment, and the stability of the entire system.
Practical application and consideration of LVC
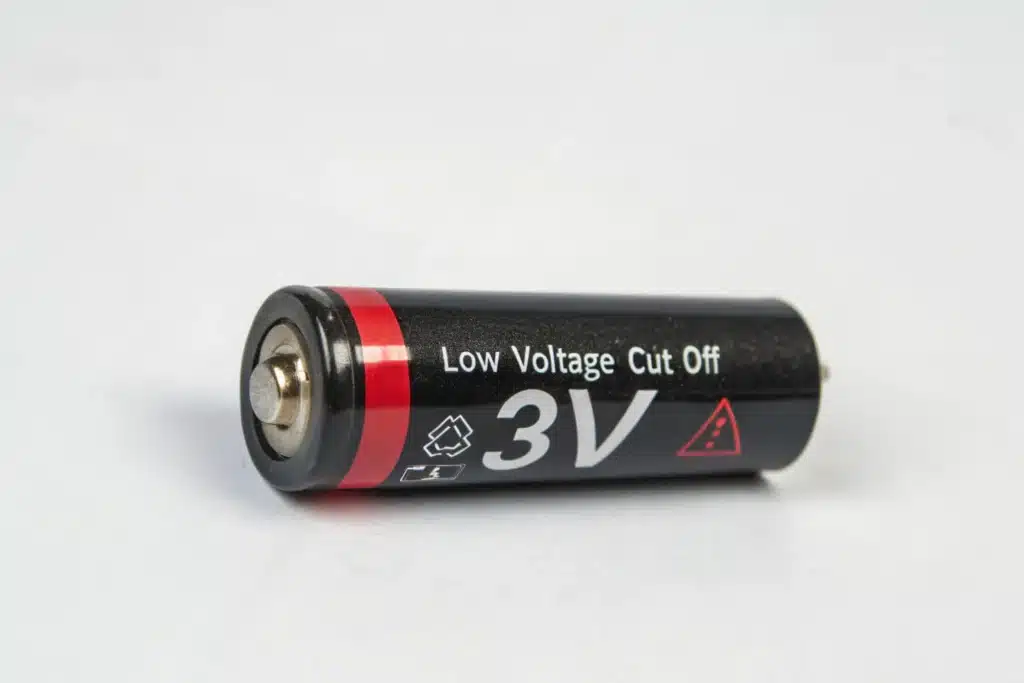

Low voltage cutoff is a key safety feature, but it is not a universal voltage value that applies to all lithium batteries. Different batteries have their own unique chemical systems and therefore have different discharge cutoff voltages.
The discharge cut-off voltage of a single-cell lipo battery is generally 2.5 ~ 3V, the safe cut-off voltage of a lifepo4 battery is 2.5V, and the minimum discharge cut-off voltage of a 18650 battery is 3V.
The only way to determine the most accurate and safest LVC voltage value for your battery is to use information provided by the battery manufacturer itself. You can find the specific setting value in the data sheet.
Relationship between LVC and Battery Management System (BMS)
In addition to LVC, is there a more comprehensive protection measure? That is the battery management system (BMS). For a battery pack consisting of multiple battery cells connected in series or in parallel, the role of the BMS circuit is crucial.
Over-discharge protection is one of the core protection functions of BMS, which can also provide over-charge protection, over-current protection, and temperature protection. Balancing function can prevent certain batteries from always being over-charged or over-discharged, maximize the capacity of the entire battery pack, and significantly extend the overall life of the battery pack.
It can also monitor battery voltage, current and temperature changes, and estimate the remaining power. Some advanced BMS can also estimate battery health.
Conclusion
Low Voltage Cutoff (LVC) is a critical line of defense for the safety and life of lithium batteries. Whether you buy a pre-made one or do it yourself, make sure that effective LVC protection measures are in place. When it comes to using lithium batteries, safety always comes first.
