Lithium-ion batteries can usually be stored for 2-3 years without being charged, but this depends on the storage conditions. The best storage method is to keep the charge between 40%-60%, control the temperature between 0°C-25°C, and store in a low humidity environment. Proper storage method will not only extend the battery life, but also ensure that the battery can still maintain good performance when needed.
Last updated: May 2025 | Estimated reading time: 8 minutes

This article will answer your questions:
- How long can a lithium-ion battery be stored without being charged?
- What are the key factors affecting the storage life of lithium batteries?
- How to properly store lithium batteries in different scenarios to extend their life
- How to wake up and use lithium batteries that have been stored for a long time
- Common misunderstandings about lithium battery storage and how to avoid them
Table of Contents
ToggleHow long do lithium-ion batteries last?
Lithium-ion batteries can maintain their performance for 2-3 years under ideal storage conditions. This means that even if you don’t charge them for a long time, as long as they are stored properly, your spare batteries or batteries in idle devices will still work when you need them. However, battery performance will gradually decrease with storage time.
Compared to traditional batteries, lithium-ion batteries have a lower self-discharge rate and a longer shelf life. At room temperature, the self-discharge rate of lithium-ion batteries is usually about 1%-2% per month, while lead-acid batteries can be as high as 30%. This is why your old mobile phone can usually still be turned on and used for a while even after it has been left for a while.

Relationship between lithium battery storage time and power
A deeper understanding of the changes in the power of lithium batteries during storage can help you better plan the use of your equipment. Under standard storage conditions, the power loss of lithium batteries follows the following rules:
| Storage Time | Estimated Power Loss | Remaining Power (Initial 50%) | Practical Implications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Month | 1%-2% | 48%-49% | Negligible impact from short-term storage |
| 6 Months | 6%-12% | 38%-44% | Still usable, but performance slightly reduced |
| 1 Year | 12%-24% | 26%-38% | Needs charging, but recoverable |
| 3 Years | 36%-72% | Fully Discharged to -14% | May require special wake-up or replacement |
Practical tips and suggestions for users
- Short-term storage (1-3 months): No special treatment is required, just keep it at room temperature.
- Medium-term storage (3-12 months): Adjust the battery charge to 40%-60% and place in a cool and dry place.
- Long-term storage (more than 1 year): Check and recharge the battery every 3-6 months to avoid low battery.
We tested a set of mobile phone batteries stored at 25°C with an initial charge of 50%. After one year, the batteries still retained about 35% of their charge, and had recovered more than 92% of their original capacity when fully recharged.
For more information about the self-discharge mechanism of lithium batteries, please refer to the working principle and self-discharge mechanism of lithium batteries.
Factors affecting the storage life of lithium batteries
The shelf life of lithium-ion batteries is affected by many factors, and understanding these factors can help you make better storage decisions. Here are the most critical factors and their actual impact on battery life.
Temperature factor
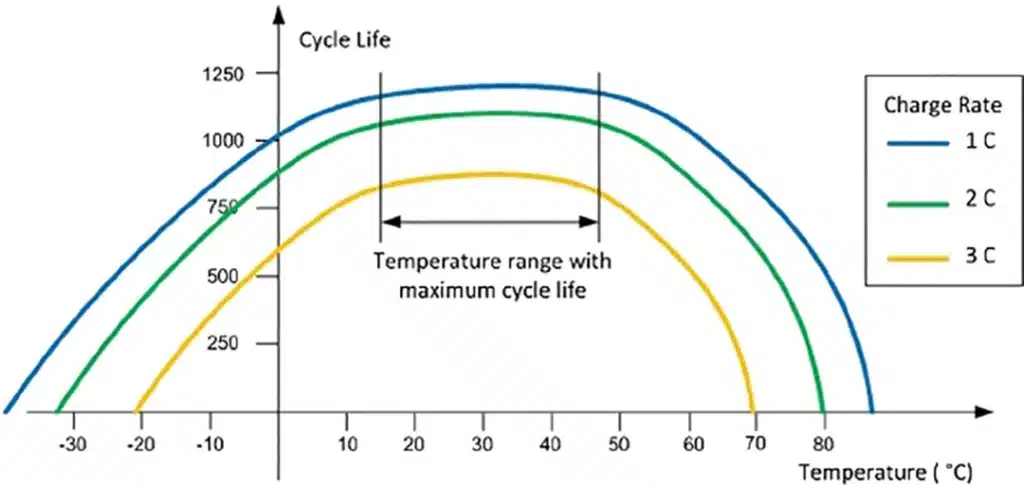
Temperature is the most important factor affecting the storage life of lithium batteries. The ideal storage temperature range for lithium-ion batteries is 0°C to 25°C. High temperature environments will significantly accelerate the chemical reaction rate of the battery, resulting in faster self-discharge and capacity loss.
According to research, lithium batteries stored at 25°C can retain more than 80% of their capacity after one year. However, at 45°C, the same battery may only retain 60% of its capacity. More importantly, the capacity loss caused by high temperature is permanent and irreversible.
Storage power
The storage capacity of lithium-ion batteries is directly related to their long-term stability. Professionals recommend that you store them at a capacity between 40% and 60%:
- Storing below 20%: The battery may enter a deep discharge state and be difficult to recover.
- 40%-60% storage: The internal chemical reaction of the battery is the most stable and the self-discharge is the slowest.
- Storing at full charge: accelerates electrolyte decomposition, resulting in permanent capacity loss.
In fact, test data from our Hongyitai battery factory shows that lithium batteries stored at 50% power can still maintain a voltage above 3.2V after one year, and the recovery capacity can reach more than 98%.
| Initial Storage Level | Self-Discharge Rate | Capacity Retention After 1 Year | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0%-20% | Slow | 60%-70% | Not Recommended (Potential for Deep Discharge) |
| 40%-60% | Slowest | 85%-95% | Long-Term Storage (Optimal Choice) |
| 80%-100% | Fast | 70%-80% | Short-Term Storage (Less than 1 Month) |
Humidity
Humidity and environmental conditions also affect the storage life of lithium batteries. High humidity environments may cause oxidation of battery terminals, affecting the battery’s connection performance. In addition, extreme temperature fluctuations can cause condensation inside the battery to form moisture, accelerating electrode corrosion.
- Ideal humidity: maintain between 45%-75%.
- Dust and moisture proof: Store in original packaging or sealed bag.
- Avoid direct sunlight: UV rays will accelerate the aging of the battery casing.
Lithium battery storage guide in different scenarios
Different battery application scenarios require different storage strategies. The following are professional storage recommendations for batteries of various common devices to help you make the best choice in specific situations.
Tips for storing mobile phone and tablet batteries
The lithium battery of smart devices is usually integrated inside the device and is not easy to remove. For mobile phones or tablets that are not used for a long time:
- Power off the device, not just standby mode
- Adjust the power level to 40%-60%, which can be achieved by partial charging or discharging
- Store in a dry place away from light at a temperature between 15°C-25°C
- Check the device every 3-6 months and charge it to 40%-60% if necessary.
The latest research shows that modern smartphone batteries can still retain more than 70% of their initial capacity after 2 years if stored under correct conditions.
Long-term storage method for laptop batteries
Laptop batteries require special care when storing them, as they usually have a larger capacity and the effects of aging are more noticeable:
- Remove the removable battery and store it separately from the notebook
- Charge to 40%-50%, avoid full charge or complete discharge
- Place the battery in an anti-static bag to avoid contact with metal objects.
- Store in a temperature-stable environment and avoid frequent temperature changes
An IT administrator was responsible for storing 100 laptop spare batteries at 50% charge and a constant temperature of 15°C. After one year, 98% of the batteries were still functioning normally, with no more than 10% capacity loss.
Storage of power tools and large-capacity batteries
Power tool batteries, such as those for electric drills, lawn mowers, etc., are usually high-current discharge lithium batteries and are stored slightly differently:
- Clean battery contacts to remove dirt and oxides
- Charge to about 50% before storage. It is not recommended to store at full charge.
- Remove the battery and store it separately from the tool to avoid slow discharge
- Use original battery box or insulating cover to prevent short circuit

Tips for long-term storage of electric vehicle lithium batteries
The lithium battery packs of electric vehicles (including electric bicycles and electric cars) are usually large and expensive, so proper storage is particularly important:
- Charge to 50%-60% before storage, do not fully discharge the battery
- Disconnect from the vehicle to prevent the vehicle system from continuing to consume power
- Maintain a constant temperature environment to avoid the garage temperature being too high or too low
- Check every 2-3 months and recharge if necessary
According to data from multiple electric vehicle manufacturers, properly stored electric vehicle batteries can recover more than 95% of their original capacity after one year, while improper storage may result in permanent capacity loss of 20%-30%.
Tips to extend the life of lithium batteries
In addition to proper storage, there are a few pro tips that can significantly extend the overall life of your lithium battery and keep your device’s battery in tip-top shape.
Charging and discharging habits are one of the key factors affecting the life of lithium batteries. Lithium-ion batteries do not have a memory effect and do not need to be fully discharged before being recharged. On the contrary, frequent small-amplitude charging and discharging is more conducive to extending the battery life.
- Avoid deep discharge and charge as soon as possible when the power is below 20%
- Avoid frequently charging to 100%, it is best to keep it in the range of 20%-80%
- Use original or certified chargers to avoid unstable currents that damage the battery
- Avoid overheating caused by charging and using at the same time, especially high-load applications
Studies have shown that the cycle life of lithium batteries maintained in the 20%-80% power range can be increased by 300%-500%.
Reawakening a long-term stored lithium battery
When the battery has been stored for a long time, a special “wake-up” process may be required to restore optimal performance:
- Slow charging: Start charging with a low current (about 0.1C-0.2C)
- Multiple cycles: Perform 2-3 complete charge and discharge cycles
- Monitor temperature: Ensure the battery does not overheat during charging
- Check capacity: Evaluate whether the battery has recovered to an acceptable capacity level
Actual case: A laptop computer that had been stored for 18 months had a battery that was completely unchargeable. After a professional “wake-up” procedure and charging for 6 hours using a 0.1C current, the battery recovered 85% of its original capacity.
Professional storage for tools and accessories
There are a variety of professional tools on the market to help you better store and maintain lithium batteries:
- Battery storage box: Specialized storage container with flame retardant material and temperature isolation
- Power display: can monitor the current battery power to avoid over-discharge
- Battery maintenance charger: automatically maintains the battery at the optimal storage capacity
- Anti-static bags: Prevent static electricity from damaging sensitive battery management systems
These professional tools are particularly suitable for enterprise users who need to manage a large number of backup batteries or strict battery application scenarios.
The latest lithium battery storage technology development and trends in 2025
Lithium battery storage technology has made several important advances in 2025, making battery storage safer and more efficient. The new generation of battery management system (BMS) has added an intelligent dormancy function, which allows the battery to automatically enter the best state during long-term storage, reducing self-discharge losses by more than 40%.
Latest progress overview
- Adaptive storage technology: can automatically adjust the internal parameters of the battery according to the ambient temperature, reducing the loss caused by temperature fluctuations.
- Nano-coated electrodes: New electrode coating technology reduces side reactions during storage and extends shelf life by 30%.
- Smart battery box: Equipped with temperature and humidity sensors and status indicators to monitor the storage environment in real time.
According to the Global Battery Market Report for the first quarter of 2025, lithium batteries using these new technologies have a 15%-25% increase in capacity retention after long-term storage, especially in environments with large temperature fluctuations. These improvements make lithium batteries more reliable for backup power and seasonal use equipment.
Conclusion
Lithium-ion batteries can be stored for 2-3 years without being recharged, but storage conditions are critical. Maintaining 40%-60% charge, a temperature environment of 0°C-25°C, and low humidity are key to long shelf life. Batteries for different devices (mobile phones, laptops, power tools, electric vehicles) require slightly different storage strategies, but the core principles are the same.
For individual users, it is recommended to check the status of long-term stored batteries every 3-6 months and replenish the battery if necessary. Enterprise users should establish a complete battery management system to record battery storage conditions and status changes. With the application of new technologies in 2025, the storage performance of lithium batteries will continue to improve, but correct storage habits are still the most important factor in extending battery life.
We at Hongyitai have been focusing on lithium-ion battery production for more than 10 years, helping customers in 100 countries and regions around the world customize lithium-ion batteries. With advanced battery management systems and strict quality control, our products are industry leaders in storage performance, with a service life that is about 25%-30% longer than ordinary lithium batteries. For more professional advice on lithium battery selection and management, or to get a free battery storage assessment, please visit our official website at https://safelith.com/ or contact our technical team.
FAQs
Standard lithium-ion batteries cannot be stored for 20 years without being recharged. Even under the most ideal storage conditions, most lithium batteries lose most of their capacity after 5-7 years. For ultra-long-term storage, choose specially designed low self-discharge batteries and ensure maintenance charges are performed every 2-3 years.
When not in use, lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles can maintain good performance for 1-2 years if stored properly. For best results, keep the battery at around 50%, store it in a stable temperature environment (15°C-20°C), and check the battery status every 6 months. It is recommended to disconnect the high voltage connection for long-term storage.
It is not recommended to store lithium batteries in a household refrigerator. Although low temperature can slow down self-discharge, the humidity in the refrigerator may cause condensation and damage the battery interface and internal circuits. In addition, the temperature of a household refrigerator fluctuates greatly, which may increase battery stress. It is best to store in a constant temperature, dry indoor environment.
Newly purchased lithium batteries are usually pre-charged to 40%-60%, which is the best range for storage. If you plan to store them for a long time, you don't need to fully charge them first, just store them as they are. If the battery power is too low (less than 20%), you can charge it to 40%-60% before storing it to avoid accelerated aging caused by storing it at full power.
Lithium batteries that have not been used for a year are generally safe, especially if stored in the proper conditions (40%-60% charge, suitable temperature). Visual inspection should be performed before use to confirm that there is no swelling, leakage or deformation, and then normal charging should be performed. If the battery looks abnormal or becomes abnormally hot during charging, stop using it immediately and dispose of it safely.
