When traveling in an RV, having a reliable power system is essential. Lithium batteries are quickly becoming the first choice for RV enthusiasts due to their superior performance, lightweight design and long life. Whether you are planning a short weekend camping trip or a long-term trip, choosing the right lithium battery will significantly enhance your RV travel experience. This guide will help you understand the types of RV lithium batteries, voltage system selection, and how to accurately determine the capacity you need.
Last updated: May 2025 | Estimated reading time: 12 minutes

This article will answer your questions:
- What types of RV lithium batteries are there, and which lithium battery is best for your RV.
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of 12V, 24V and 48V voltage systems, and how to choose.
- How to accurately calculate the battery capacity required for your RV to avoid insufficient power or overinvestment.
- Performance, life and cost-effectiveness comparison of mainstream RV lithium battery products on the market.
- How to choose supporting system components for optimal performance and safety.
- Key factors and common misunderstandings to consider before purchasing lithium batteries.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat are the types of RV lithium batteries
Lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries are currently the best choice for RV use because of their excellent safety performance and ultra-long life cycle of up to 3000-5000 times. Compared with traditional lead-acid batteries, lithium batteries are lighter (about 1/3 of lead-acid batteries), more efficient (charge and discharge efficiency can reach 98%), and can be deeply discharged without damaging the battery life.
There are three main types of RV lithium batteries: lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), ternary lithium (NMC) and lithium manganese oxide (LMO). Although ternary lithium has a higher energy density, lithium iron phosphate batteries are more outstanding in terms of safety and cycle life.
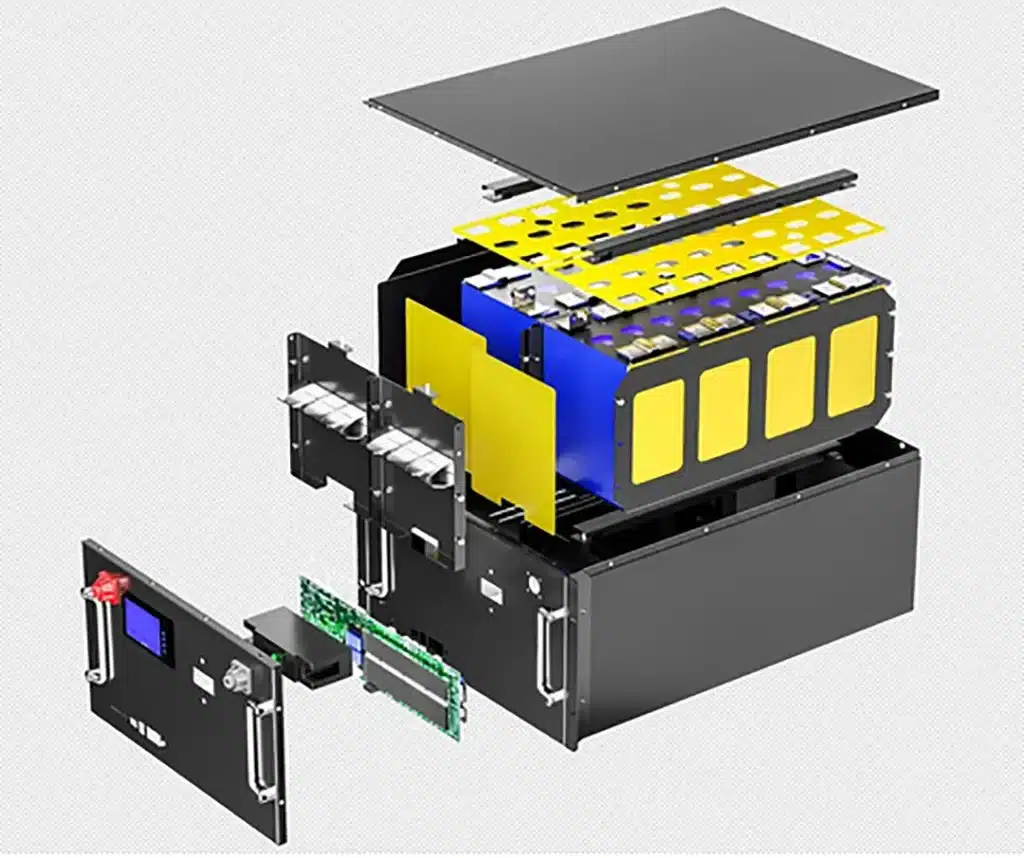
Comparison of different lithium battery types:
| Battery Type | Cycle Life | Safety Performance | Energy Density | Practical Significance to You |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) | 3000-5000 cycles | Extremely High | Medium | Most economical for long-term use, highest safety |
| Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC) | 1000-2000 cycles | Moderate | High | Small size, lightweight, but higher safety risks |
| Lithium Manganese Oxide (LMO) | 500-1000 cycles | High | Low | Low cost but short lifespan, not recommended for long-term use |
Practical tips and suggestions for users:
- Long-term travel users: Choose lithium iron phosphate batteries. Although the initial cost is higher, the average cost per cycle is the lowest.
- Safety-conscious families: Stick to lithium iron phosphate batteries, which remain stable even under extreme temperatures and physical shocks.
- Short-term weekend camping users: Consider lithium iron phosphate batteries with smaller capacity to balance investment and practicality.
A full-time RV traveler upgraded his lead-acid battery to lithium iron phosphate, which not only reduced the weight of the vehicle by about 60 kg, but also shortened the charging time from 8 hours to 2.5 hours, while increasing the available power by about 35%.
RV voltage system selection
The 48V system has significant advantages in large-capacity applications, especially when you need more than 10 kWh of capacity or frequently use high-power appliances. However, for most ordinary users, the 12V system is still a practical choice due to its wide compatibility and mature accessory ecosystem.
The choice of RV voltage system directly affects your power efficiency, charging speed and cable cost. When choosing, you need to consider your actual power needs, budget and the possibility of future expansion.
Analysis of advantages and disadvantages of different voltage systems:
12V System:
- Advantages: Compatible with most RV accessories, mature market, low initial cost.
- Disadvantages: Large line loss when high power is applied, low charging efficiency, and requires thicker cables.
- Suitable users: Users with battery capacity requirements less than 5 kWh, limited budget, and occasional RV users.
24V System:
- Advantages: Balanced compatibility and efficiency, wire diameter can be reduced, and charging speed is moderate.
- Disadvantages: Some accessories need to be converted, and there are relatively few market options.
- Suitable users: Users with battery capacity between 5-10 kWh and moderate RV use.
48V System:
- Advantages: fastest charging speed, minimum line loss, supports high-power consumption, and is compact.
- Disadvantages: requires more voltage conversion equipment, and relatively few accessories on the market.
- Suitable users: users with battery capacity exceeding 10 kWh and frequent or long-term use of RVs.

Use the following questions to find the voltage system that’s best for you:
How much battery capacity do you need?
- Less than 5 kWh: 12V system is preferred
- 5-10 kWh: 24V system is considered
- More than 10 kWh: 48V system is recommended
Do you often use high-power electrical appliances (air conditioners, microwave ovens, etc.)?
- Yes: 48V system is preferred
- No: 12V or 24V system may be sufficient
What is your budget?
- Limited budget: 12V system has the lowest initial investment.
- Medium budget: 24V system balances performance and cost.
- Sufficient budget: 48V system is the most cost-effective for long-term use.
How to accurately determine the battery capacity you need for your RV
This requires calculating your daily electricity consumption and considering the need for independent power days. Most RV users find a balance between 4-10 kWh, but heavy users may need more than 15 kWh of capacity.
Accurately calculating battery capacity is a key step to avoid overinvestment or under-capacity. This is not only related to your return on investment, but also directly affects your travel experience.
Use the table below to estimate your daily electricity needs:
| Device | Power (Watts) | Daily Usage (Hours) | Daily Energy Consumption (Watt-hours) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LED Lights (5) | 25W (Total) | 4 hours | 100Wh |
| Refrigerator | 60W | 8 hours (Run Time) | 480Wh |
| Laptop | 70W | 3 hours | 210Wh |
| Water Pump | 100W | 0.5 hours | 50Wh |
| Microwave | 1000W | 0.3 hours | 300Wh |
| Air Conditioner (1P) | 1000W | 3 hours | 3000Wh |
| Total | – | – | 4140Wh (Approx. 4.14 kWh) |
Actual required battery capacity = daily power consumption × number of independent power days ÷ depth of discharge × (1 + safety margin)
For example: 4.14 kWh × 2 days ÷ 80% (discharge depth) × 1.2 (20% safety margin) = 12.42 kWh
Practical tips and suggestions for users:
- Weekend camping users: 4-6 kWh is usually enough (2-3 days of independent electricity use).
- Holiday travel users: 8-10 kWh is ideal (4-5 days of independent electricity use).
- Full-time travel users: consider 12-20 kWh of electricity capacity (used with solar energy system).
A family of four was equipped with a 10-kWh lithium battery and a 400W solar panel during a 7-day self-driving trip. Without using air conditioning, it fully met daily electricity needs, including refrigerator, lighting, charging and occasional use of rice cookers.
Comprehensive comparison of mainstream RV lithium batteries on the market
The quality and performance of RV lithium batteries on the market vary significantly. Choosing well-known brands and professional manufacturers can significantly reduce safety risks and subsequent maintenance costs. Currently, the products on the market are mainly divided into three price ranges: high-end brands, mid-range cost-effective and economical.
When evaluating different products, one should not only look at capacity and price, but also factors such as the BMS management system, shell material, connector quality and after-sales service.
| Brand | Advantages/Features | Typical Price (100Ah) | Practical Significance for You |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brand A | Top-tier BMS, 10-year warranty, remote monitoring | $900-1100 | Highest safety and longest lifespan |
| Brand B | Extreme environment adaptability, smart temp control | $850-1000 | Suitable for use in various climate conditions |
| Brand C | Integrated Management System, Bluetooth Monitoring | $800-950 | Easy for real-time monitoring and management |
Cost-effective product recommendation
| Brand | Advantages/Features | Typical Price (100Ah) | Practical Significance for You |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brand D | High-quality cells, 5-year warranty | $600-750 | Good balance of performance and price |
| Brand E | Easy to install, good compatibility | $550-700 | Suitable for DIY installation users |
| Brand F | Waterproof casing, shockproof design | $500-650 | Suitable for off-roading and harsh environments use |
How to identify high quality lithium batteries
- Check the BMS system: A high-quality BMS system can provide overcharge, over-discharge, short circuit and temperature protection.
- Battery cell quality: Original brand batteries (such as LG, Panasonic, Samsung) usually provide more stable performance.
- Consistency processing: Good batteries will undergo strict cell sorting and matching to improve overall performance.
- Housing and connectors: A sturdy housing and high-quality connection terminals are essential for long-term use.

A user bought a cheap, unbranded lithium battery. After using it for 6 months, he found that the charging speed slowed down and the capacity decreased by about 30%. Testing found that the battery cell was unbalanced due to quality problems with the BMS system. Eventually, he had to replace the battery with a new one. The total cost exceeded that of directly purchasing a mid-range product.
To learn more about LFP lithium batteries, please check out our lifepo4 battery products.
Supporting system component selection
The quality and matching of supporting system components directly determine the performance and safety of the entire power system. The right charger, inverter and monitoring system can maximize the potential of your lithium battery and extend its service life.
A complete RV power system consists of four core parts: battery pack, charging system, inverter and monitoring system. These components need to work in coordination with each other to achieve efficient and safe power supply.
- AC charger: Choose a smart charger that supports the charging curve of lithium batteries and matches the battery capacity (usually 25-40A charger for every 100Ah).
- Solar controller: MPPT controllers are 15-30% more efficient than PWM, especially in low light conditions.
- Isolator and DC-DC charger: Use products designed for lithium batteries to avoid undercharging or overcharging.
Inverter selection points:
| Inverter Type | Suitable Scenarios | Typical Price (2000W) | Practical Significance for You |
|---|---|---|---|
| Modified Sine Wave Inverter | Simple appliances, non-sensitive equipment | $150-300 | Economical, but may not be suitable for all devices |
| Pure Sine Wave Inverter | Sensitive electronics, medical equipment | $400-800 | Same power quality as household power, suitable for all devices |
| Bidirectional Inverter/Charger Combo | High-end systems, needs simplified wiring | $1000-2500 | Space-saving, highly integrated, convenient to use |
A high-quality monitoring system can display the following key information in real time:
- Remaining battery capacity and power percentage
- Real-time charge and discharge current and power
- Battery temperature and health status
- Estimated remaining usage time
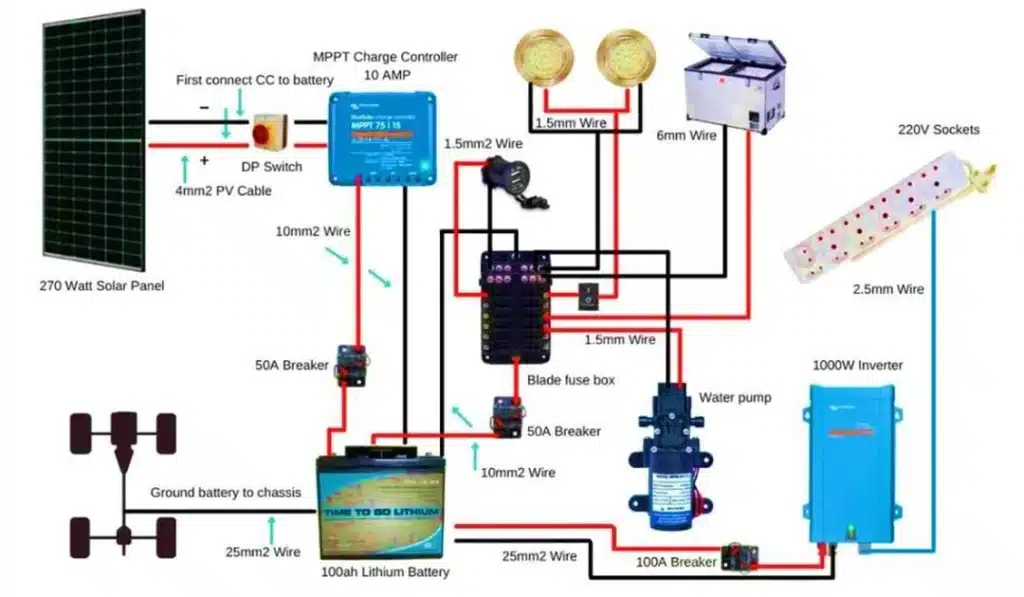
Practical tips and suggestions for users:
- Charging equipment matching: Make sure all charging equipment supports lithium battery charging profiles.
- Wire specification selection: Select wires of appropriate specifications according to system voltage and maximum current to avoid overheating.
- Temperature management: In extreme temperature environments, consider adding a battery heating or cooling system.
- Protection circuit: Add circuit breakers and fuses at key points to increase system safety.
One RV enthusiast used a 48V system with a 500A battery bank and 3000W inverter, able to run both the air conditioning and induction furnace, while achieving 80% energy self-sufficiency during the day with a 1200W solar panel.
The ultimate guide to buying decisions
Purchasing a lithium battery is a significant investment that requires a balance of short-term costs and long-term value. On average, a high-quality lithium battery can last 8-10 years, and despite the higher initial investment, the long-term total cost of ownership (TCO) is typically lower than repeatedly replacing lead-acid batteries.
Before making your final decision, consider the following key factors to ensure you get the best return on your investment.
Actual needs and future plans:
- Current electricity demand
- Possible demand changes in the next 2-3 years
- Possibility of system expansion
Budget and long-term value:
- Initial investment budget
- Long-term use cost (cost per cycle)
- Return on investment cycle
Installation and compatibility:
- Compatibility with existing systems
- Difficulty and expertise required for installation
- Cost of necessary additional accessories
Brand and after-sales:
- Brand reputation and market feedback
- Warranty period and terms
- After-sales service network and response speed
The latest development and trend of RV lithium battery technology in 2025
The RV lithium battery market is experiencing rapid development in 2025, with overall prices on a downward trend, while performance and integration continue to improve. According to the latest market data, lithium iron phosphate battery prices have fallen by about 18% in the past two years, while cycle life and charging speed continue to improve.
- New battery materials: Semi-solid electrolyte technology is beginning to be applied to high-end RV batteries, providing higher safety and energy density.
- Smart BMS evolution: AI-based battery management systems can predict battery health status and optimize charging and discharging strategies.
- Fast charging technology: The latest fast charging protocol in 2025 enables specific models of lithium batteries to be charged to 80% in 40 minutes.
- Integration trend: The integrated design of lithium batteries, inverters, and solar controllers simplifies installation and use.
The RV lithium battery market is expected to maintain an average annual growth rate of about 15% between 2025 and 2030. The main drivers of growth include the increase in the RV travel population, the increase in consumer demand for sustainable energy solutions, and the continued advancement of battery technology.
Conclusion
RV lithium batteries are an important investment to enhance your travel experience, and choosing the right type, capacity, and voltage system is essential to meet your power needs. Lithium iron phosphate batteries are the best choice due to their excellent safety and service life, while the 48V system provides significant advantages for large-capacity applications.
We at Hongyitai have been focusing on lithium-ion battery production for more than 10 years, helping customers in 100 countries and regions around the world to customize lithium-ion batteries. We provide a full range of RV lithium battery solutions, from 12V to 48V, from 50Ah to 400Ah, to meet the needs of different users. Each of our products has been rigorously tested and comes with industry-leading warranty services. Click here for more details.
FAQs
Definitely worth it. Although the initial investment of lithium batteries is higher (about 2-3 times that of lead-acid batteries of the same capacity), the long-term use cost of lithium batteries is actually lower considering the service life (lithium batteries can reach 3000-5000 cycles, while lead-acid batteries usually only have 300-500 cycles). In addition, lithium batteries are light in weight, small in size, and charge quickly, which significantly improves the user experience.
This depends on your electricity usage habits and independent electricity needs. Generally speaking, 4-6 kWh is enough for weekend camping users, 8-10 kWh is ideal for holiday travel users, and 12-20 kWh is required for full-time travel users. The calculation method is to add up the daily power consumption of all electrical appliances, then multiply it by the number of days you want to use electricity independently, and then divide it by 80% (recommended discharge depth).
The 12V system has the best compatibility and is suitable for small capacity requirements; the 48V system charges faster, has a thinner wire diameter, supports greater power, and is suitable for large capacity (more than 10 kWh) applications. At the same power, the current of the 48V system is only 1/4 of that of the 12V system, and the line loss is about 1/16 of that of the 12V system, which significantly improves efficiency when using high-power electrical appliances. When choosing, you need to consider your capacity requirements, budget, and compatibility of electrical equipment.
When the capacity of a lithium battery drops below 70-80% of its original capacity, or the charging time increases significantly, or a stable voltage cannot be maintained, it usually indicates that the battery is nearing the end of its service life. Most high-quality lithium batteries can be used for 8-10 years or 3000-5000 charge and discharge cycles under normal use conditions.
Installation of a small 12V system is feasible for users with basic electrical knowledge. However, for high voltage (such as 48V) or large capacity systems, it is recommended to seek professional installation. In any case, be sure to follow the installation guide and use the correct size wires and protection devices to ensure safe operation of the system.
