Have you ever encountered this situation? Holding a lithium battery in your hand, such as a cylindrical battery, with “18650” written on it, as well as “3.7V”, “3000mAh”, or even a mark like 10C, you may not understand the meaning behind these numbers.
In fact, if you can’t understand these numbers and letters, it’s not just as simple as choosing the wrong model. It may cause you to buy an incompatible battery, which may cause your device to be unusable or performance to be compromised, or even damage your device or even bring some safety hazards. The purpose of this article is to help you disassemble the common labels on these batteries, such as model, voltage, capacity, discharge capacity, etc., one by one, so that you can easily understand and have a clear idea.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhy understanding battery numbers is important
We know those numbers look complicated, but why should you bother trying to understand them? It turns out that understanding the details is more important than you think, for a few reasons:

Compatibility. Imagine buying a new battery for your flashlight, drone, or other device, only to find that it is the wrong size and won’t fit in your device! It’s also possible that the voltage (that number marked with V) is wrong. Using a battery with the wrong voltage can cause your device to not work at best, or even burn out in an instant. Therefore, understanding the size code (such as 18650) and the nominal voltage (such as 3.7V) is the first insurance to ensure that the battery you buy can be used and will not damage your device.
Safety. Lithium batteries have a high energy density. If you don’t understand their operating limits, such as the maximum charge and discharge current they can withstand (which is usually related to the parameter called C rate), you may accidentally overcharge, over-discharge, or short-circuit the battery. These operations may cause the battery to heat up, bulge, and shorten its lifespan dramatically. In extreme cases, they may even cause dangers such as smoke and fire.
Performance matching. Do you want your device to last longer? Or do you need a battery that can provide powerful instant power for your power tools and racing drones? This information is also hidden in the numbers! Capacity (mAh or Ah) directly determines how long the device can be used. The discharge rate (C-rating) determines how quickly the battery can release energy (i.e. power). Choosing these two parameters correctly can ensure that your device can work for a long time and burst out enough power when needed.
Correct replacement. When the original battery of your device is worn out and needs to be replaced, you can understand the label on the old battery. You can confidently find a new battery with the same voltage, equivalent (or higher) capacity, the same size, and the discharge capacity (C-rating) that meets the requirements, and easily complete the replacement without the trouble of buying the wrong one.
Correct replacement. When the original battery of your device is worn out and needs to be replaced, you can understand the label on the old battery. You can confidently find a new battery with the same voltage, equivalent (or higher) capacity, the same size, and the discharge capacity (C-rating) that meets the requirements, and easily complete the replacement without the trouble of buying the wrong one.
Detailed explanation of battery numbers and symbols
We will now reveal the numbers on the battery label one by one. We will help you interpret them layer by layer, just like peeling an onion.
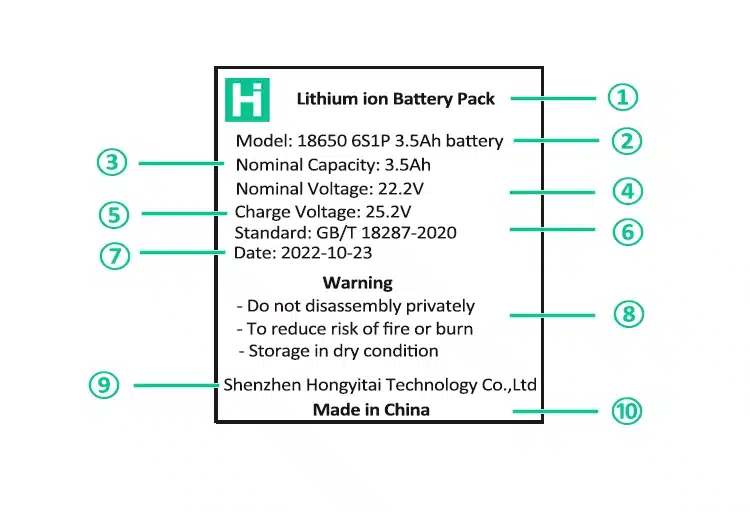
Model & Size: This is directly related to whether the battery can be installed in your device. For the most common cylindrical 18650 battery, ’18’ represents a diameter of about 18mm, ’65’ represents a length of about 65mm, and the last ‘0’ usually indicates that it is cylindrical. Like 21700 batteries (thicker and longer, commonly used in high-performance flashlights or electric vehicles), 14500 (about the same size as AA batteries). Square or soft-pack batteries. Their naming rules may be different. The most common ones are expressed by thickness, width, and length, and the unit may be millimeters (mm). For example, 606090 may mean 6.0mm thick, 60mm wide, and 90mm long.
Nominal voltage: It represents the average voltage of the battery when it is discharged, which is the key to matching the device. The most common nominal voltage of lithium-ion batteries is 3.7V, and the voltage of lithium iron phosphate batteries is 3.2V.
Charging voltage: It represents the voltage when the battery is fully charged. The charging voltage of lithium-ion battery is 4.2V, and the charging voltage of lithium iron phosphate battery is 3.65V.
Capacity and voltage are the core performance parameters of lithium batteries, directly determining their operating voltage range and discharge duration.
Discharge cut-off voltage: It represents the lowest safe voltage for battery discharge. The cut-off voltage of lithium-ion batteries is generally 3V, and that of lithium iron phosphate batteries is 2.5V.
Capacity: It represents how long the battery can be discharged, which is what we call battery life. The unit is Ah or mAh. 1Ah = 1000mAh. The corresponding power, in Wh, is calculated as follows: Power (Wh) = Capacity (Ah) × Nominal Voltage (V).
Discharge rate: The unit is C-rating. For example, for a 3000mAh (3Ah) battery, the current of 2C discharge is 3 * 2 = 6A. Drones, power tools, high-power electronic cigarettes and other equipment require the battery to output a large current instantly.
Battery chemistry type. Sometimes there will be abbreviations on the label, such as ICR, IMR, INR, NCM or LiFePO4/LFP, which represent different internal chemical materials that affect the performance of the battery. IMR/INR usually has a stronger discharge capacity, LiFePO4 is safer and has a longer life but lower voltage.
Production date & batch number: Batteries usually have a production date or batch number. Lithium batteries will naturally age over time, and their capacity and performance will decrease. Therefore, knowing the production date can help determine whether the battery is new and give you an expectation of its condition.
How to use lithium battery digital
Combined with the meaning behind the numbers and symbols on the lithium battery labels mentioned above, you can use the knowledge you have just learned to make the right decisions when you encounter specific problems in real life.
Replace old batteries
Before replacing a battery, check the key parameters. The physical size/model must match, otherwise it will not fit. The nominal voltage (V) must be exactly the same! This cannot be wrong, otherwise it may damage the device. The capacity (mAh/Ah) should preferably be the same as the original, or slightly larger to extend the battery life. The discharge rate (C-rating), especially for equipment such as power tools and drones, the new C-rating must be at least equal to or higher than the old one, otherwise low power may occur, resulting in poor performance and battery overheating.
Selecting batteries for your new product
This is not a simple replacement, but a choice based on the actual needs of your product. You need to think about the following questions:
How many volts (V) does your project need to operate? This is the basis for selecting a battery voltage.
How long do you want your project to run? Estimate how much capacity (mAh/Ah) you will need based on the device’s power consumption and expected battery life.
Estimate how much current (A) your device will require at maximum load? Then divide this current value by the capacity (Ah) of your selected battery to get the minimum required C-rate. Choosing a battery with an insufficient C-rate may result in project failure or battery damage.
After choosing the right battery based on the above parameters, don’t forget to check the physical dimensions to make sure it will fit in your battery compartment.
Charger compatibility
Voltage matching: The output voltage of the charger must accurately match the battery’s charging cut-off voltage. For example, to charge a lithium battery with a nominal battery voltage of 3.7V, a charger with an output voltage of 4.2V must be used. Direct charging with a 5V USB port is absolutely not allowed (unless there is a dedicated charging management circuit).
Current matching: The output current of the charger cannot exceed the maximum charging current allowed by the battery. This current is usually expressed in C (such as 0.5C, 1C). You need to refer to the battery specification or follow general safety recommendations (such as charging at no more than 1C). Charging with excessive current will seriously affect the battery life and may cause overheating or even danger.
Frequently asked questions
After learning so much about battery numbers, you may still encounter some special situations or have some questions. Below we will answer some common questions and reiterate some safety rules that must be followed.
- The label on the battery has worn off and cannot be seen clearly. What should I do?
You can try to find the manual for your device, which usually contains the battery specifications. Then, search online to see if you can find a matching battery based on the device model or any visible markings on the battery. Be careful to measure, and if you are very experienced and have the right tools, you can measure physical dimensions and voltage. If you really can’t confirm the specifications, it is best not to use this battery for safety reasons.
- Why is there no C rate marked on my battery?
This often means that this is a standard or low-rate discharge battery. You should never assume that it will be used in high-current applications, such as high-performance drones, power tools, or high-power e-cigarettes.
- Short circuit is strictly prohibited. You must use a matching and qualified charger to avoid over-discharge and properly dispose of discarded batteries.
Summarize
In short, it is key to understand the voltage (V), capacity (Ah/mAh/Wh), size and discharge rate (C-rating) on the battery label. Understanding this information can really help you choose the right battery, ensure safety, and get the best performance from your device. If you still don’t understand, please contact us to help you understand the information behind it.
