A lithium polymer battery—often called a LiPo battery—is a type of rechargeable battery. It’s lightweight, thin, and packs a lot of power in a small size. You’ll find it in drones, RC toys, power banks, and other portable electronics. Unlike older battery types, it uses a soft, flexible pouch instead of a hard case.
But while LiPo batteries are powerful, they also need to be charged carefully. Charging them the wrong way can lead to swelling, overheating, or even fire. It can also shorten the battery’s life and lower its performance.
This article will show you how to charge your LiPo battery safely. You’ll learn what tools to use, what steps to follow, and what mistakes to avoid. These tips will help protect your battery — and everything around it.
At Hongyitai, we’ve worked in the battery field for over 10 years. We know how LiPo batteries behave, and we’re here to help you avoid the common risks.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding lithium polymer batteries
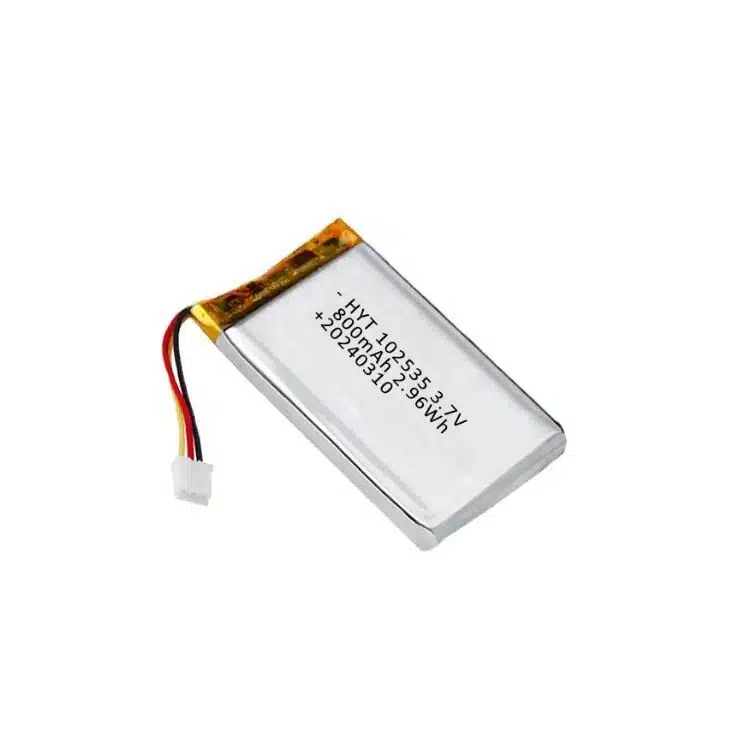

A lithium polymer (LiPo) battery is a type of rechargeable lithium battery. Unlike standard lithium-ion batteries that use a liquid electrolyte, LiPo batteries use a gel-like polymer electrolyte. This makes them lighter, more flexible in shape, and ideal for small devices where space and weight matter.
LiPo batteries work by moving lithium ions between two parts: the cathode (positive side) and the anode (negative side). When you charge the battery, the ions move in one direction. When you use the battery, they move back. This movement is what stores and releases energy. You can study our li-polymer battery product over here.
But LiPo batteries are sensitive. They need to be charged and handled carefully. If you overcharge the battery or use the wrong charger, the battery can become unstable. If it’s punctured, crushed, or exposed to heat, it may swell or even catch fire.
For example, if you charge a 3.7V LiPo battery past 4.2 volts per cell, it can start to degrade inside. This might not show right away, but over time the battery will lose capacity, heat up faster, and not last as long. That’s why overcharging is one of the biggest risks.
LiPo batteries work well when treated properly — but small mistakes can lead to big problems. That’s why safe charging is so important. In the next section, we’ll explain exactly why safe charging matters and how it protects both your battery and your device.
Why safe charging matters
Charging a lithium polymer battery might seem simple, but doing it the wrong way can lead to serious problems. LiPo batteries store a lot of energy in a small space. That’s what makes them useful—and also what makes them risky if not handled with care.
One of the biggest dangers is thermal runaway. This happens when the battery gets too hot during charging and can’t cool down fast enough. The heat builds up and causes a chain reaction inside the battery. If it goes too far, the battery may catch fire or explode.
Here’s why safe charging really matters:
- Helps prevent fire by lowering the risk of thermal runaway
- Stops the battery from swelling or leaking if it’s charged too much
- Keeps your battery healthy longer by avoiding stress and damage
- Protects your device and space from heat, smoke, or fire
Charging safely doesn’t take much effort. But it does make a big difference in how well your battery performs and how long it lasts.
Safe charging setup
Before you charge a lithium polymer battery, it’s important to set things up the right way. A safe setup helps prevent mistakes that could harm the battery — or cause a fire.
Start by using the right charger. Every LiPo battery has a specific voltage and current rating. Your charger should match those numbers exactly. Using the wrong charger can cause the battery to overheat or become unbalanced.
If your battery has more than one cell, you should use a balance charger. This kind of charger makes sure each cell charges evenly. Uneven charging can lead to weak spots or swelling over time.
Here’s a quick guide for common LiPo battery types:
- 1S = 3.7V (single-cell)
- 2S = 7.4V (2 cells)
- 3S = 11.1V (3 cells)
- 4S = 14.8V (4 cells)
Also, check for built-in safety features. Many LiPo packs include a protection circuit module (PCM). A common example is a small chip like the DAA IC paired with 8205A MOSFETs. These parts help control overcharging, over-discharging, and short circuits. Some even monitor the battery’s temperature and shut it down if things get too hot.
When possible, charge the battery inside a fireproof LiPo bag or metal box. These containers are designed to hold in flames if something goes wrong. Place them on a surface that doesn’t burn, like stone or metal.
A safe charging setup doesn’t take long to prepare. But it gives you peace of mind and helps your battery work better and last longer.
Step-by-step charging guide

Charging a lithium polymer battery the right way starts with a few careful steps. Following these steps helps prevent damage and keeps your battery safe.
Here’s your step-by-step charging guide:
- Inspect the battery. Look closely for any signs of swelling, leaks, cracks, or rust around the terminals. If the battery is damaged in any way, don’t charge it. Damaged LiPo batteries can fail suddenly and are not safe to use.
- Set your charger correctly. Check the label on your battery for its voltage and capacity. Then, adjust the charger to match. Make sure the voltage is set for the correct number of cells (e.g., 7.4V for 2S). Use a charge rate that fits your battery—usually 1C is safe. That means a 2000mAh battery should be charged at 2.0 amps.
- Connect the battery. Use the proper connector and plug the battery into the charger. Make sure the wires are not loose and that the connection is solid. If you’re using a balance charger for a multi-cell battery, plug in both the main lead and the balance plug.
- Choose a safe charging spot. ut the battery in a fireproof LiPo bag or a metal box. Charge it on a surface that doesn’t burn, like tile or concrete. Make sure the area is open and well-ventilated so heat can escape.
- Stay nearby. on’t leave the battery alone while it’s charging. If it gets hot, smells strange, or swells, unplug it right away and move it to a safe place.
- Unplug when full. When the charger shows the battery is full, disconnect it. Leaving it on the charger too long can cause stress and shorten the battery’s life.
These simple steps can help your LiPo battery stay healthy and safe to use.
Charging best practices

Charging a lithium polymer battery safely is not just about using the right tools. Good habits also help your battery last longer and work better. These best practices are easy to follow and make a big difference over time.
a. Charge at room temperature. LiPo batteries should be charged in a space that’s not too hot or too cold. The ideal range is 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). Learn futher temperature affect. Avoid charging below 0°C (32°F) or above 45°C (113°F). Cold temperatures slow down the chemical reaction inside the battery, while heat can increase pressure and lead to swelling or leaks.
b. Set the right charge rate. Use a 1C charge rate unless your battery says it can handle more. “1C” means charging at a rate equal to the battery’s capacity. For example, a 2200mAh battery should charge at 2.2 amps. Fast charging might save time, but it adds stress to the battery and can reduce its lifespan unless the battery is designed for it.
c. Don’t fully discharge before charging, It’s best to stop using your battery when the voltage drops to 3.5 volts per cell. Going lower than that, especially below 3.0V, can damage the inside of the battery.
Deep discharges increase the risk of swelling, especially if you then try to recharge right away.
d. Store at 50–60% charge. If you won’t be using your battery for several days or more, store it at around 50–60% charge. This helps reduce wear on the cells. Some chargers have a “storage mode” that automatically charges or discharges the battery to the right level.
These habits may seem small, but they help keep your battery safe and working well over time.
Mistakes to avoid
Charging a LiPo battery the wrong way can lead to serious problems. To stay safe, it’s important to know what not to do. Below are some common mistakes that should always be avoided:
Do not use damaged or bloated batteries. A battery that’s swollen, leaking, or has broken wires is unsafe. Charging it can lead to heat buildup, fire, or even explosion. Damaged cells should be recycled, not reused.
Limit charging on flammable surfaces like wood or fabric. If something goes wrong during charging, heat or sparks can catch nearby surfaces on fire. Always charge on a non-flammable surface like tile, metal, or stone.
Exceeding voltage or cell count settings. Setting your charger to a higher voltage than your battery needs can overcharge the cells. This increases internal pressure and may cause swelling or thermal runaway. Always match your settings to the battery label.
Mixing different capacity cells in one pack. Each cell charges and discharges at a different rate. If they’re not evenly matched, one cell can become overcharged or over-discharged, which increases the chance of failure.
Avoiding these mistakes helps protect your battery, your device, and your space from harm.
What to do if something goes wrong
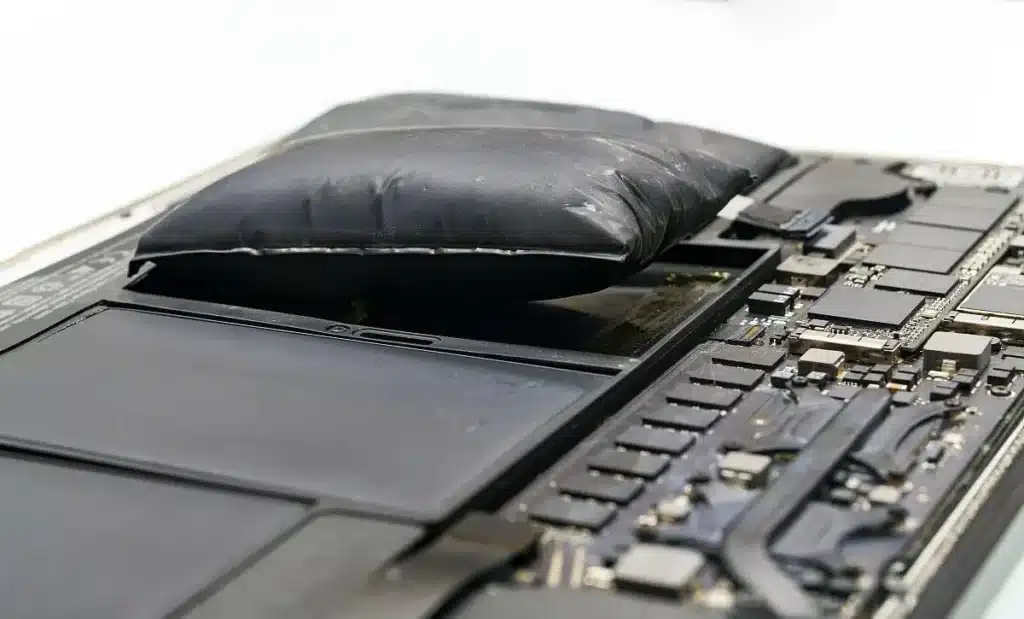

Even with careful charging, problems can still happen. Knowing what to do helps keep you safe.
If the battery gets hot. Stop charging right away. Unplug the charger and move the battery to a fire-safe area. Let it cool completely before touching or using it again.
If swelling appears. A swollen battery is unsafe. Do not charge or use it again. Place it in a fireproof container and take it to a battery recycling center as soon as possible.
If there’s a fire. Use a Class D fire extinguisher if available. If not, cover the battery with sand to smother the flames. Do not use water—water can make a lithium fire worse and spread the heat.
Never puncture the battery or throw it in the trash. Damaging the outer shell can release dangerous chemicals. Always handle used or damaged batteries with care.
Quick action during problems helps prevent bigger risks.
Conclusion
Charging your lithium polymer battery the right way makes a big difference. It helps your battery last longer and lowers the risk of swelling, overheating, or fire. A few smart habits—like using the right charger, setting it up safely, and staying nearby—can prevent serious problems.
Always use the proper tools. Follow each step carefully. And don’t take shortcuts, even if you’ve charged batteries many times before. Safe charging protects not just your battery, but also your device and space.
By now, your questions about safe LiPo charging should be answered. You know what to do, what to avoid, and how to act if something goes wrong.
For long-term safety, it also helps to start with a battery you can trust. At Hongyitai, lithium polymer batteries are a core part of what we do. We’ve been in the battery field for over 10 years, and our products are well-reviewed by engineers and users worldwide.
FAQs
Can I charge a LiPo battery overnight?
Not recommended unless using a smart charger with auto shut-off and monitoring.
What’s the best charge rate?
A 1C rate is safest. Check battery label or datasheet.
Can I charge a swollen battery?
No. Dispose of it at a battery recycling center.
Is it safe to leave the charger plugged in after charging?
Unplug both battery and charger after full charge to avoid risk.
How do I know when a LiPo is fully charged?
4.2V per cell for a full charge. Most smart chargers will indicate "full."
