When you use a lithium-ion battery in your device, you may have heard the advice to never fully discharge it. But why does this matter? The truth is, how you manage your battery’s charge can significantly affect its lifespan and performance. While lithium-ion batteries are designed for long-term use, improper charging habits can lead to problems down the road. This is where many people make mistakes, assuming that fully discharging their battery will somehow improve its longevity or performance.
In this article, we’ll clear up common myths about lithium-ion batteries and explain the impact of fully discharging your device. You’ll learn why deep discharges can damage your battery, and why partial charging is a better practice for keeping your battery healthy. We’ll also cover the role of Battery Management Systems (BMS) in protecting your battery, and how to prevent damage from over-discharging.
You’ll have a clear understanding of how to properly care for your battery and avoid the mistakes that could shorten its life. Whether you’re using your battery in a phone, laptop, or other device, we’ve got you covered.
With over 10 years of experience in the battery industry, we’ve seen firsthand how proper care can make a significant difference in battery performance and longevity. Trust our knowledge to guide you in making smarter decisions about battery care, so you can get the most out of your lithium-ion batteries.
Table of Contents
ToggleDeep charging VS shallow charging
Deep charging and shallow charging are terms used to describe how much charge a lithium-ion battery gets during each cycle. Deep charging refers to charging a battery after it has been drained to a very low percentage, usually below 20%. On the other hand, shallow charging is when you charge the battery before it gets too low, typically when it’s between 40% and 80% of its full capacity.
Both deep and shallow charging can affect the battery’s health, but in different ways. Deep charging, especially when done frequently, can cause long-term damage to the battery. When a lithium-ion battery is repeatedly drained to a very low level, it forces the battery to go through more charge cycles. This stresses the battery’s internal chemical structure and can result in capacity loss, meaning the battery won’t hold as much charge over time. Furthermore, deep discharges can cause the battery to lose its ability to efficiently charge and discharge, ultimately shortening its lifespan.
Shallow charging, however, is much gentler on the battery. By charging the battery before it gets too low, you prevent it from going through unnecessary full charge cycles. This helps to preserve the battery’s overall health and prolong its lifespan. With shallow charging, the battery’s internal components don’t experience as much wear and tear, leading to more consistent performance over a longer period.
To maintain a healthy lithium-ion battery, the best practice is to avoid deep discharges. Charging your device when it reaches around 20% to 30% and unplugging it when it hits 80% is often considered the optimal strategy. This balance keeps your battery in a healthy state without overcharging or over-discharging. For more tips on how to safely charge your lithium-ion battery, check out this guide on safely charging your lithium polymer battery.
The risk of battery damage from complete discharge
When a lithium-ion battery is fully discharged, it can lead to serious long-term damage. This occurs because the battery’s internal chemistry is designed to maintain a specific voltage range. When the battery drops below a certain voltage, it can cause the internal structure to become unstable. Over time, this can reduce the battery’s ability to hold a charge, making it less efficient.
One of the main risks of a complete discharge is the potential for the battery to fail to recharge. Once a battery drops below a critical voltage, the battery management system (BMS) may not be able to protect it from further damage, and the battery might not take a charge again. The actual risks of deep discharge include:

- Inability to recharge: If the battery voltage falls too low, the battery may fail to accept a charge, rendering it useless.
- Permanent capacity loss: A deep discharge can cause the battery’s capacity to decrease permanently, meaning it won’t hold as much power over time.
- Cell imbalance: The internal cells may become unbalanced after a deep discharge, causing them to work inefficiently or even fail completely.
- Reduced cycle life: Frequent deep discharges shorten the number of full charge cycles the battery can handle, decreasing its overall lifespan.
Repeated full discharges can have cumulative long-term effects. Over time, the stress on the battery’s components can cause irreversible damage. The battery may not hold a charge as well as it did when it was new, leading to shorter usage times and less efficiency. Additionally, as the battery’s performance decreases, it may become more prone to overheating, which can lead to safety concerns.
To avoid these risks, it’s best to avoid letting your battery completely discharge. Instead, try to charge it when it reaches around 20% to 30% to preserve its health and longevity.
Battery management system (BMS) protection
A Battery Management System (BMS) is a crucial component of modern lithium-ion batteries. It is responsible for monitoring and managing the health and safety of the battery by ensuring it operates within safe parameters. The BMS tracks several important factors, such as voltage, temperature, and charge cycles, to protect the battery from conditions that could cause damage or reduce its lifespan.

One of the key roles of the BMS is to protect the battery from deep discharge damage. When the battery voltage drops too low, the BMS steps in to prevent further discharge, ensuring the battery doesn’t go below a certain threshold. Here are a few examples of how the BMS helps prevent deep discharge-related damage:
- Voltage Monitoring: The BMS constantly monitors the battery’s voltage and will disconnect the load if it detects that the voltage is too low. This prevents the battery from discharging below its safe voltage level, avoiding permanent damage.
- Preventing Over-Discharge: If the voltage drops too far, the BMS will stop the battery from discharging any further, essentially “shutting it down” to avoid deep discharge.
- Balancing Cells: In multi-cell batteries, the BMS ensures that all cells discharge at the same rate. This prevents one cell from being over-discharged, which could cause it to fail.
While the BMS provides essential protection, it does have limitations. For example, the BMS cannot prevent damage if the battery has been left in a fully discharged state for an extended period. If a battery is deep discharged and left in that state for too long, the BMS may no longer be able to restore the battery to full functionality. Additionally, while the BMS can stop the battery from discharging too much, it doesn’t prevent the damage caused by frequent deep discharges, which can still lead to long-term degradation of the battery’s capacity and performance.
Understanding how the BMS works helps highlight why it’s so important to avoid full discharges whenever possible, even with the system in place to protect the battery.
Is deep discharge a fire hazard
Fully discharging a lithium-ion battery can lead to safety risks, but these risks are not always immediate or obvious. While deep discharges are primarily known for reducing battery lifespan and causing performance issues, they can also contribute to dangerous situations under certain conditions. However, it’s important to understand how deep discharges may indirectly lead to more severe problems, such as thermal runaway.
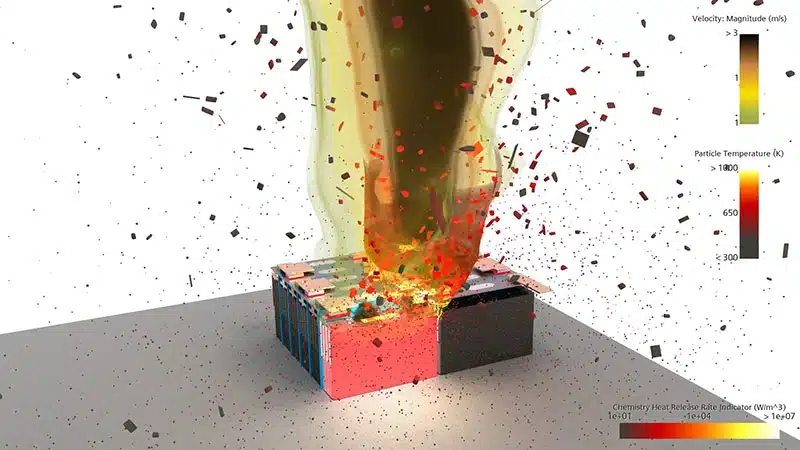

Thermal runaway is a condition where the battery’s temperature rapidly increases, potentially leading to a fire or explosion. While this process is more commonly associated with overheating, overcharging, or physical damage, deep discharges can play a role in making batteries more susceptible to thermal runaway. When a battery is deeply discharged, its internal components become unstable. This instability can create conditions that make the battery more vulnerable to overheating, especially if it is charged improperly or exposed to damage later on.
Thermal runaway typically happens when a battery’s internal temperature exceeds safe levels, often due to internal short circuits, excessive charge or discharge rates, or poor battery design. If a deeply discharged battery is then subjected to physical stress or improper charging, this imbalance can lead to excessive heat generation. Overheating can further damage the battery, triggering thermal runaway, where the battery heats uncontrollably, potentially causing it to catch fire or explode.
Fortunately, modern lithium-ion batteries are equipped with various safety measures, including Battery Management Systems (BMS). The BMS plays a key role in reducing the risk of thermal runaway by monitoring the battery’s voltage and temperature. It cuts off power if the battery approaches unsafe levels, preventing deep discharges from leading to dangerous conditions.
Additional safety features, such as heat protection and pressure relief valves, also help mitigate the risks, allowing gases to escape safely and reducing the likelihood of an explosion. While deep discharges are not directly responsible for fires, they can contribute to conditions that increase the risk of thermal runaway, which is why it’s important to avoid letting the battery drop too low in the first place.
How a full discharge affects battery capacity
Frequent full discharges can have a significant impact on the capacity of your lithium-ion battery. When a battery is repeatedly drained to very low levels, it goes through more full charge cycles. Each cycle gradually wears down the internal components, leading to a reduction in the battery’s ability to hold a charge. Over time, this means that the battery won’t last as long on a full charge, and its overall capacity will decline.
The capacity degradation is largely influenced by the voltage levels within the battery. Lithium-ion batteries have a specific voltage range they must remain within to operate efficiently. When the voltage drops too low, the internal chemical reactions inside the battery become unstable. This instability causes the battery to lose its ability to efficiently store and release energy, leading to a permanent reduction in capacity. A full discharge often causes the battery to dip into these low voltage ranges, accelerating the degradation process.
On the other hand, partial discharges help preserve the battery’s capacity over time. When you charge your battery before it gets too low—usually when it’s between 20% and 30%—you avoid forcing it into these harmful low voltage levels. Partial discharges reduce the stress placed on the battery, allowing the internal chemical reactions to stay balanced. This means the battery will be able to retain more of its original capacity for a longer period.
By avoiding frequent full discharges, you can significantly extend the lifespan of your battery. It’s better to keep your battery within the optimal charging range of 20%-80%. This practice helps maintain the battery’s capacity, ensuring it continues to perform well for as long as possible.
Reduced charging efficiency
Fully discharging a lithium-ion battery can lead to reduced charging efficiency over time. When a battery is drained completely, it forces the internal components to operate at low voltage levels. This stress can cause chemical imbalances within the battery, which makes it harder for the battery to recharge efficiently. As the battery ages, the internal resistance increases, meaning it takes longer to charge, and the battery may not reach its full capacity as easily.
The relationship between battery health and charging time is closely tied to the internal resistance and the battery’s ability to hold and release charge. A battery in good health typically charges quickly and reaches full capacity without significant loss of energy. However, as the battery undergoes repeated full discharges, the internal chemistry begins to break down. This breakdown results in a higher internal resistance, which in turn leads to longer charging times and lower efficiency. Essentially, the battery has to work harder to store energy, and much of the energy is lost during the process.
When a battery is frequently fully discharged, you may notice that it takes longer to charge it or that it doesn’t reach a full charge as quickly as before. This is due to the increased internal resistance and the degradation of the battery’s chemistry.
In contrast, partial discharges help maintain charging efficiency. When you charge your battery before it drops too low, you prevent it from experiencing the chemical imbalances caused by deep discharges. Partial discharges allow the battery to stay within a healthier voltage range, meaning it doesn’t suffer the same level of wear and tear. As a result, the charging time remains relatively consistent, and the battery can recharge more quickly and efficiently. By avoiding deep discharges and charging when the battery is between 20% and 30%, you preserve both battery health and charging efficiency for a longer time.
Does it shorten battery life
Regularly deep discharging your lithium-ion battery can have serious long-term consequences on its lifespan. Each time you fully discharge the battery, you put additional stress on its internal components, leading to gradual degradation. Over time, this constant strain reduces the battery’s ability to hold a charge and perform at its best. The effects of regular deep discharges include:
- Permanent capacity loss: The battery will hold less charge, meaning shorter usage times between charges.
- Reduced overall lifespan: Repeated full discharges accelerate the wear and tear on the battery, causing it to degrade faster.
- Higher internal resistance: Deep discharges increase the internal resistance, which can lead to slower charging times and less efficient performance.
- Increased risk of overheating: The stress from deep discharges can make the battery more prone to heat buildup, potentially leading to safety concerns.
A complete discharge significantly impacts the cycle life of a lithium-ion battery. Each time the battery is charged from a low voltage to full capacity, it counts as one cycle. Lithium-ion batteries are designed to last for a certain number of cycles, typically around 500 to 1,000 cycles before their capacity starts to decline. However, when you regularly deep discharge your battery, you use up more of these cycles. This reduces the overall lifespan of the battery and means it will need to be replaced sooner than expected.
To understand the difference between shallow and deep discharges, here’s a simple comparison of their effects on battery lifespan:
| Factor | Shallow Discharge (20%-80%) | Deep Discharge (0%-100%) |
| Cycle Life | Longer cycle life | Shorter cycle life |
| Capacity Retention | Better capacity retention | Faster capacity loss |
| Charging Efficiency | Maintained charging efficiency | Reduced charging efficiency |
| Battery Lifespan | Extended lifespan | Reduced lifespan |
As shown in the table, shallow discharges help preserve the battery’s capacity and overall lifespan, making it a better practice for keeping your battery healthy over the long term. By avoiding frequent full discharges, you can maximize the number of charge cycles your battery goes through, helping it last longer and perform better.
Mitigating damage from over-discharge: best practices
To protect your lithium-ion battery from over-discharge, it’s important to follow some simple best practices that will help preserve its health and extend its lifespan. Here are a few steps you can take to prevent damage:
- Avoid letting your battery reach 0%: Try to keep your battery above 20-30% charge at all times. Charging it before it gets too low prevents deep discharges and helps maintain its efficiency.
- Charge regularly, but don’t overcharge: While it’s important to charge your battery, avoid keeping it plugged in at 100% for extended periods. Unplug the device when it hits around 80% to help reduce stress on the battery.
- Use appropriate chargers: Always use the charger that comes with your device or a certified replacement. Using non-certified chargers can lead to overcharging or inefficient charging, which can damage the battery.
Another way to protect your battery is by using tools and apps to monitor its health. Many smartphones, laptops, and other devices come with built-in battery health management features. Additionally, third-party apps can help you keep track of your battery’s charge cycles and overall health. Some apps, like AccuBattery (for Android) and Battery Health (for iOS), provide useful insights into how your charging habits are affecting your battery.
By adopting these best practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of over-discharge and ensure that your battery stays in good condition. Regular charging, monitoring, and proper care will help your battery last longer and perform better over time.
Conclusion
In this article, we’ve discussed the many reasons why deep discharges are harmful to your lithium-ion battery. Repeatedly draining your battery to 0% puts unnecessary stress on its internal components, leading to permanent capacity loss, reduced efficiency, and a shorter lifespan. We also explored how deep discharges increase the risk of damaging your battery and how it impacts overall performance, including charging times and cycle life.
To ensure that your battery stays healthy and lasts as long as possible, it’s essential to follow some simple charging habits. Remember to avoid letting your battery reach 0%, charge it regularly between 20% and 80%, and use the proper charger for your device. By practicing these habits, you can significantly extend your battery’s lifespan and maintain optimal performance.
For more information on how to prevent battery damage and handle your batteries safely, be sure to check out our guide on battery risks and prevention.
Following these best practices is the best way to ensure that your lithium-ion battery continues to serve you well over the long term. Proper care and mindful charging will help your battery perform at its best, so you can get the most out of your device.
We hope this article has answered your questions and helped you understand how to take better care of your battery. If you still have any further questions or need assistance, feel free to reach out to us at Hongyitai. We’re here to help!
