Lithium polymer batteries and lithium ion batteries are essentially in the same family, but they differ significantly in structure, performance and application scenarios. Lithium polymer batteries are packaged in aluminum plastic film, which is lighter and more flexible, while traditional lithium ion batteries use metal casings and have higher energy density. The latest research in 2025 shows that the two battery technologies have their own advantages in different applications.
Last updated: May 2025 | Estimated reading time: 10 minutes
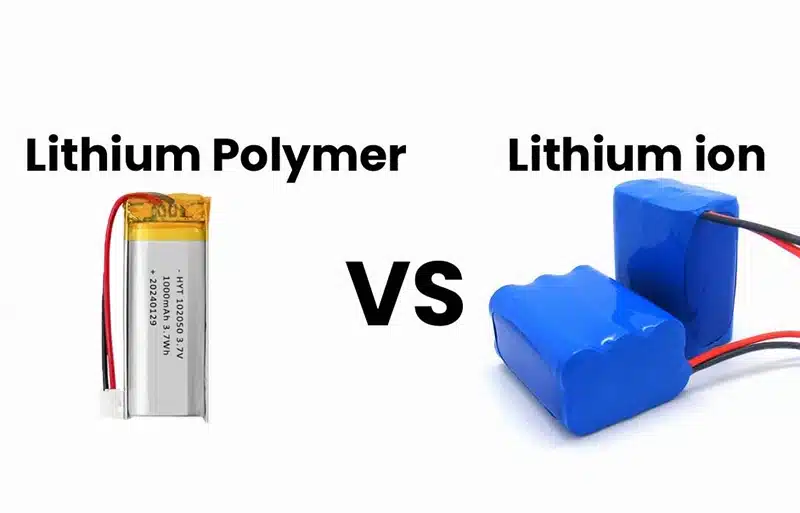
This article will answer your questions:
- The difference between the basic structure and working principle of lithium polymer and lithium ion batteries.
- How to quickly identify different types of lithium batteries by appearance.
- Which battery performs better in devices such as mobile phones, notebooks and drones.
- The difference between the two batteries in safety, cycle life and charging characteristics.
- The latest battery technology development trends and price trends in 2025.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is lithium polymer battery?
Lithium polymer battery (LiPo) is a type of lithium-ion battery that uses a gel or solid polymer electrolyte instead of a traditional liquid electrolyte. The battery is packaged in a flexible aluminum-plastic film instead of a rigid metal casing, allowing it to be made into a variety of shapes and sizes.
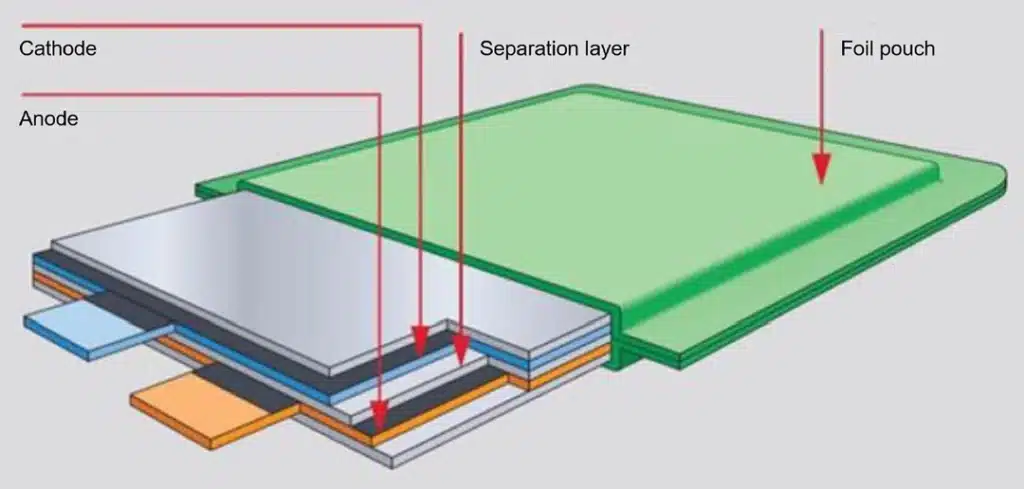
The electrochemical principle of lithium polymer batteries is similar to that of traditional lithium ion batteries, both of which rely on the movement of lithium ions between the positive and negative electrodes to generate current. The difference lies in the form of the electrolyte:
| Feature | Lithium Polymer Battery | Traditional Lithium-Ion Battery | Practical Significance for You |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrolyte Form | Gel or Solid Polymer | Liquid | Safer, Reduced Leakage Risk |
| Packaging Material | Aluminum Plastic Film | Metal Case (Steel/Aluminum) | Lighter, More Flexible Design |
| Internal Space Utilization | High (Approx. 90%) | Medium (Approx. 80%) | Larger Capacity for the Same Volume |
Practical tips and suggestions for users:
- When purchasing equipment: If you are looking for thinness and high safety, give priority to products using lithium polymer batteries.
- Identification method: Lithium polymer batteries are usually flat, have a certain degree of flexibility, and are mostly packaged in silver aluminum plastic film.
- Safe use: Still need to avoid puncture, overcharging and high temperature environment.
A 2025 flagship phone reduces battery thickness by 2.1mm while increasing battery capacity by 8%, thanks mainly to the latest generation of lithium polymer battery technology, making the phone thinner and lighter while having longer battery life. Find out our li-polymer battery product.
What is lithium-ion battery
Lithium-ion battery is a rechargeable battery encapsulated in a metal case. It uses a metal case (steel or aluminum case) for physical protection and structural support, uses liquid electrolyte, and is usually cylindrical or square. This is the earliest commercialized lithium battery technology and is still the preferred power solution for many high-power devices. We can customize li-ion battery packs based on your specific needs.
Lithium-ion batteries can be divided into two categories according to the shell material and shape:
- Steel-shell lithium-ion batteries: mainly include common cylindrical batteries such as 18650, 21700 and other models, which are widely used in high-power equipment.
- Aluminum-shell lithium-ion batteries: usually square, mostly used in equipment with certain thickness requirements.
| Type | Typical Applications | Energy Density | Practical Significance for You |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steel Case (18650) | Power Tools, Laptops | 250-300 Wh/kg | High energy density, suitable for devices needing long battery life |
| Aluminum Case (Prismatic) | Electric Vehicles, Energy Storage Systems | 220-280 Wh/kg | High space utilization, suitable for high-capacity applications |
| Polymer | Smartphones, Tablets | 150-200 Wh/kg | Thin and lightweight design, suitable for portable devices |
Practical tips and suggestions for users:
- Equipment selection: For equipment that requires high power output (such as power tools, high-power power banks), choose lithium-ion battery products.
- Identification method: Steel-shell lithium-ion batteries are usually cylindrical, while aluminum-shell batteries are mostly square, and feel hard and inelastic.
- Charge and discharge management: Avoid complete discharge, and the best use range is to keep the charge between 20%-80%.
The 100W fast-charging power bank launched by a certain brand uses 21700 steel-shell lithium-ion batteries instead of lithium-polymer batteries. The reason is that in high-power fast-charging scenarios, the discharge performance and thermal management of lithium-ion batteries are more advantageous.
Comparison between Li-polymer battery and Li-ion battery
The following is a comparison of the differences between these two batteries from multiple angles:
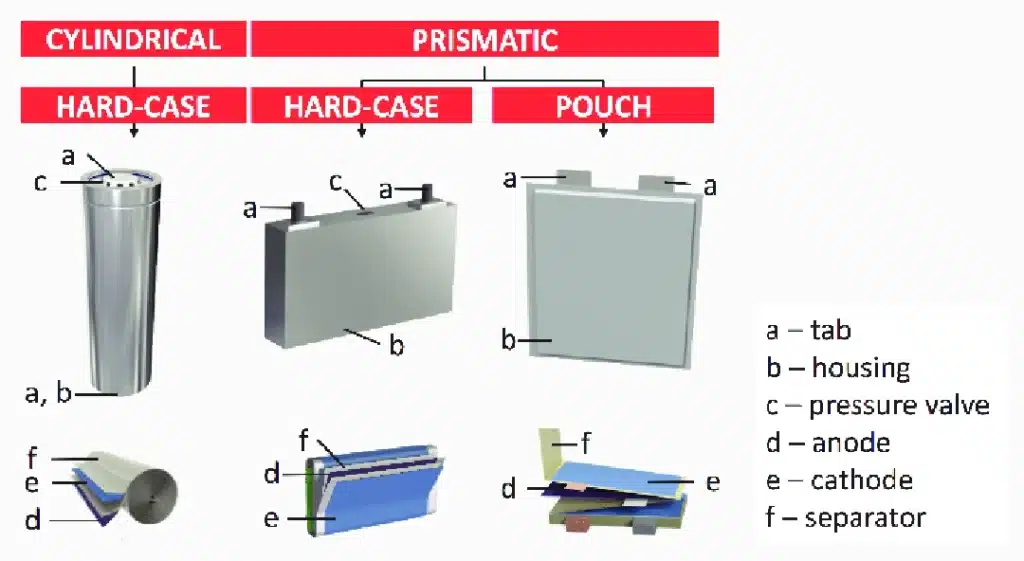
Shell material
Lithium polymer batteries use a thin aluminum-plastic composite film as the casing, while lithium-ion batteries use a stronger metal casing. This fundamental difference directly affects the battery’s weight, safety characteristics and application flexibility.
Research on battery technology in 2025 shows that major breakthroughs have been made in aluminum-plastic film packaging technology. The strength of the aluminum-plastic film of modern lithium polymer batteries has increased by 35%, while the thickness has been reduced by 15%, making the new generation of lithium polymer batteries both lighter and more durable.
The aluminum-plastic film of lithium polymer batteries will swell or crack to release pressure in extreme cases, but will not explode like metal casings.
| Case Material | Advantages | Disadvantages | Suitable Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Plastic Film (Polymer) | Lightweight, Flexible, High Safety | Poor Puncture Resistance, High Cost | Smartphones, Tablets, Wearable Devices |
| Steel Case (Lithium-Ion) | Robust and Durable, Low Cost | Heavy, Fixed Shape | Power Tools, Backup Power Supplies |
| Aluminum Case (Lithium-Ion) | Good Heat Dissipation, High Volume Utilization | Relatively Heavy, Limited Shape | Electric Vehicles, Large-Scale Energy Storage |
Size and shape
One of the biggest advantages of lithium polymer batteries is that they are available in a variety of shapes and sizes, which can be customized according to device requirements, while lithium-ion batteries are mostly standard geometries. This flexibility allows product designers to maximize the use of limited space.
Space utilization is a key factor in modern electronic device design. Lithium polymer batteries can be made into square, curved and rectangular shapes, allowing them to fit into devices with specific battery compartments, such as ultra-thin laptops, curved smart watches or irregularly shaped wireless headphones.
Capacity and energy density
In general, lithium polymer batteries have large capacity, but the truth is more complicated. Under the same external dimensions, the capacity of lithium polymer batteries is usually 10-15% higher than that of steel-cased lithium-ion batteries and 5-10% higher than that of aluminum-cased batteries, mainly due to their higher internal space utilization.
However, from a pure energy density (energy stored per unit weight) perspective, conventional lithium-ion batteries actually perform better:
| Battery Type | Energy Density (Wh/kg) | Typical Capacity Range | Practical Implications for You |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium-Ion (High-Nickel Ternary) | 250-300 | Larger Capacity Range | Suitable for devices requiring long runtimes. |
| Lithium Polymer | 150-200 | Medium Capacity | Provides larger capacity within limited space. |
Weight and volume efficiency
Lithium polymer batteries are approximately 40% lighter than steel-cased lithium batteries of the same capacity and approximately 2% lighter than aluminum-cased batteries, making them ideal for weight-sensitive devices.
The latest research in 2025 shows that advanced lithium polymer batteries can achieve higher volumetric energy density, storing up to 730 milliwatt-hours of energy per cubic centimeter, an increase of nearly 15% over 2022. This can provide longer battery life in the same volume.
Electrical performances
Lithium polymer batteries typically have lower internal resistance than traditional lithium-ion batteries, which results in several distinct performance advantages:
- Higher discharge efficiency: Low internal resistance means less loss during discharge, improving energy utilization efficiency.
- Lower heat generation: Reduce internal energy loss and lower battery operating temperature.
- Better fast charging performance: Able to withstand higher charging currents and support faster charging.
The latest data shows that the internal resistance of high-quality lithium polymer batteries can be as low as 35 milliohms, which is about 25% lower than that of steel-shell lithium-ion batteries of the same capacity.
| Performance Metric | Lithium Polymer Battery | Lithium-Ion Battery | Impact on Your Daily Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Internal Resistance | Lower (35-50mΩ) | Higher (45-70mΩ) | Lithium Polymer supports faster charging. |
| Self-Discharge Rate | 3-5%/month | 8-10%/month | Lithium Polymer retains charge longer in storage. |
| Quick Charge Capability | Excellent | Good | Lithium Polymer charges faster. |
Cycle life
The average lithium polymer battery in 2025 will provide 500-1200 charge and discharge cycles, while the latest lithium-ion battery technology provides 500-5000 cycles, depending on the specific chemistry and usage conditions. The lifespan is a key indicator of the long-term value of batteries.
The difference in battery life depends mainly on the internal chemical materials and manufacturing process, rather than just the battery form factor. Lithium iron phosphate batteries excel in cycle life, while lithium polymer batteries have an advantage in comfort and safety for daily use.
| Battery Type | Cycle Life (Cycles) | Estimated Lifespan | Suitable Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium Polymer | 800-1200 | 2-3 years of typical use | Consumer electronics, frequently replaced devices |
| Lithium-Ion (Standard) | 500-1000 | 2-3 years of typical use | Most portable devices |
| Lithium-Ion (LFP) | 2000-5000 | 5-10 years | Long-term use devices, energy storage systems |
Safety mechanism
Lithium polymer batteries are generally safer than traditional lithium-ion batteries, largely because of their flexible casing and gel-like electrolytes. In extreme cases, they are more likely to release pressure by swelling rather than exploding.
Modern lithium polymer batteries use an advanced multi-layer protection design, including:
- Thermal circuit breaker: Automatically cuts off the current when the battery temperature is too high.
- Overvoltage protection: Prevents the charging voltage from exceeding the safe range.
- Short circuit protection: The internal isolation layer prevents direct contact between the positive and negative electrodes.
These safety features make lithium polymer batteries suitable for wearable devices and portable products that may be subjected to physical shock.
Practical safety advice for users:
- Exposion treatment: If you find a bulging battery, stop using it immediately and dispose of it safely.
- Charging habits: Use original or certified chargers and avoid charging in high temperature environments.
- Physical protection: Avoid dropping or squeezing the device, especially lithium polymer battery devices.
After a well-known brand of drone upgraded its battery system from lithium polymer to high-performance lithium-ion batteries in 2024, its flight time increased by 23%, but its weight increased by 18%, demonstrating the trade-offs between the two technologies in practical applications.
The latest application trends in 2025 show that lithium polymer and lithium ion batteries are being fully reflected in different fields according to specific needs:
| Device Type | Main Battery Choice | Reason for Choice | Practical Usage Advice |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smartphone | Lithium Polymer (LiPo) | Lightweight, Shape Customization, High Safety | Replace every 2 years (generally) |
| Laptop | Hybrid (Both Li-Po & Li-ion) | Depends on Thinness vs. Battery Life Needs | Choose based on usage habits |
| Drone | High-End: LiPo, Entry-Level: Li-ion | High Discharge Rate vs. Cost Balance | <30W use LiPo, >80W use Li-ion |
| Power Tools | Primarily Lithium-ion (Li-ion) | Cost-Effective, High Current Discharge Capability | Prioritize well-known brands for safety |
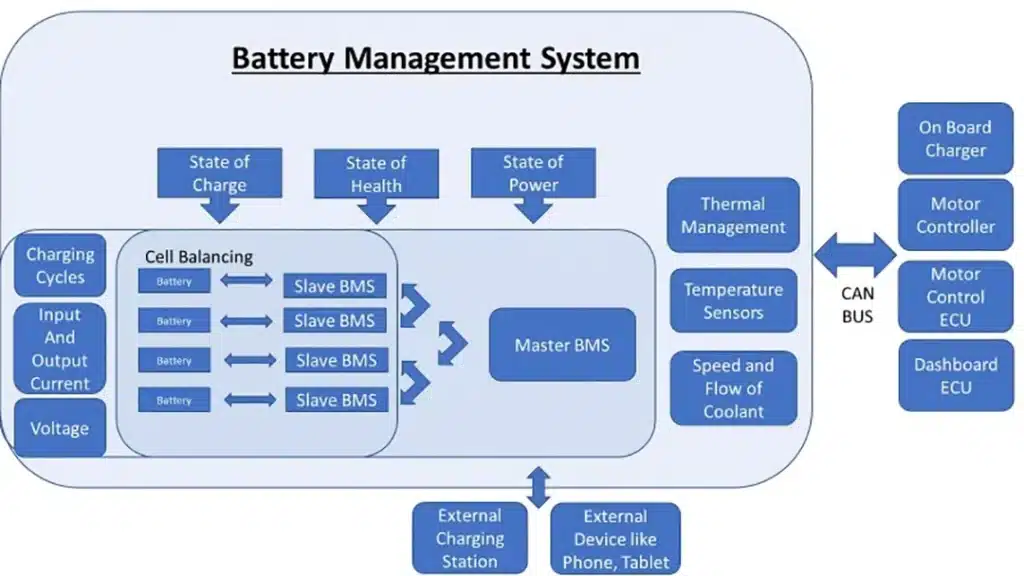
| Electric Vehicle (EV) | Almost Always Lithium-ion (Li-ion) | Cost-Effectiveness, Energy Density, and Scalable Production | Pay attention to the quality of the Battery Management System (BMS) |
When choosing a device, knowing the type of battery it has is crucial to predicting the user experience. For example, choosing a power bank for different scenarios:
- Daily commuting: Lithium polymer power banks are lighter and more portable.
- Long-distance travel: Lithium-ion power banks have larger capacity and longer battery life.
- Emergency fast charging: Lithium-ion batteries perform more stably in high-power scenarios.
Cost
The manufacturing cost of lithium polymer batteries is usually 10-30% higher than that of lithium-ion batteries of the same capacity, which is mainly affected by the complexity of the production process and the cost of materials. However, with technological advances and large-scale production, this price gap is gradually narrowing.
According to the latest market data in 2025, the price of lithium batteries is generally on a downward trend:
- The price of lithium-ion battery packs has dropped to about $85/kWh.
- The price of lithium-polymer battery packs is about $95-110/kWh.
- It is expected that by 2027, the price gap between the two battery technologies will further narrow to within 10%.
Conclusion
Lithium polymer batteries and lithium ion batteries each have their own advantages. Choosing which battery technology should be based on your specific needs and usage scenarios, rather than simply judging which one is “better”. Here is a selection guide:
Reasons to choose lithium polymer battery:
- Pursuing thin and light design and flexible shape
- High requirements for safety
- Require faster charging speed
- Small device size, requiring customized battery shape
Reasons to choose lithium-ion batteries:
- Emphasis on long service life
- Requires higher energy density and endurance
- Limited cost budget
- Applied in high-power devices or extreme environments
Battery technology in 2025 is developing towards safety, high energy density and long life. The latest semi-solid and solid-state battery technologies are expected to be commercialized in the next few years, bringing greater performance leaps.
We, Hongyitai, have been focusing on lithium-ion battery production for more than 10 years, helping customers in 100 countries and regions around the world to customize lithium-ion batteries. We provide comprehensive battery solutions, from standard battery components to fully customized special application power systems. Click on our products to view more information.
FAQs
The risk of explosion of lithium polymer batteries is significantly lower than that of traditional lithium-ion batteries. Due to the flexible aluminum-plastic film shell, lithium polymer batteries are more likely to swell and release pressure in extreme cases rather than explode. However, puncture, overcharging and high temperature environments must still be avoided to ensure safety.
Generally, lithium polymer batteries charge faster because they have lower internal resistance and can withstand higher charging currents. In 2025, lithium polymer batteries can support a 10C charging rate (i.e., charging is completed in 10 minutes), while most lithium-ion batteries are best charged at a rate of 1~3C (1 hour).
Battery bulging is a serious safety warning. Whether it is a lithium polymer or lithium ion battery, you should stop using it immediately and replace it. Bulging indicates that an abnormal chemical reaction has occurred inside the battery, and continued use may pose a safety hazard.
