RS232 and RS485 are undoubtedly the two most widely used serial communications, but their design concepts and applicable scenarios are very different. The purpose of this article is to sort out the core differences between these two standards, from distance, speed to networking capabilities, and ultimately help you make the most appropriate choice based on actual application needs.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is RS232
You can think of RS232 as a very classic communication method that allows two electronic devices to talk directly through a cable. It has been around for many years, and its official standard name is EIA/TIA-232.
RS232 is a point-to-point communication, used for one device to directly connect to another device for one-to-one communication. It is full-duplex, which is one of its advantages, meaning that two devices can send and receive data at the same time.
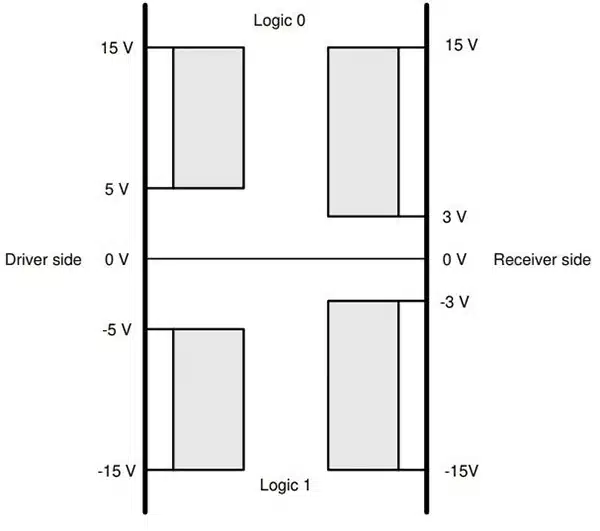
It uses an unbalanced signal, which is also its limitation. It generates a voltage (positive or negative voltage) relative to the ground line on a signal line to represent 0 or 1, and has weak anti-interference ability. The communication distance of RS232 is usually very short, theoretically only 15 meters (about 50 feet).
What is RS485
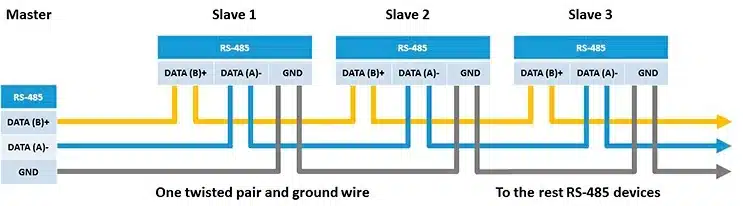
RS485 allows you to connect multiple devices on the same signal line, theoretically up to 32 load devices can be connected. The most common RS485 is half-duplex mode, because multiple devices share the same pair of transmission lines, they cannot send and receive data at the same time. Just like a walkie-talkie, either talk or listen, you need to take turns.
RS485 uses two signal lines (usually marked as A and B) to transmit differential signals together. The receiving end is concerned with the voltage difference between the two lines, rather than their respective voltages to ground. If there is electromagnetic interference in the outside world, it usually affects both the A line and the B line at the same time, but the voltage difference between them does not change much. It is precisely because of this feature that the transmission distance of RS485 can be very long, with a standard of up to 1200 meters (about 4000 feet).
Core feature comparison: RS232 vs. RS485
Below is a comprehensive comparison of RS232 and RS485.

Communication mode: RS232 is point-to-point communication, one device can only communicate with another device directly. RS485 is a multi-point design, you can connect multiple devices to the same cable to form a network bus.
Duplex mode (can talk and listen at the same time): RS232 is full-duplex, two devices can send and receive data at the same time using different lines without interfering with each other. RS485 is half-duplex, because all devices share the line, they must take turns to either send or receive, and they cannot work synchronously.
Signal mode and anti-interference: RS232 uses unbalanced signals, the voltage between the signal line and the ground line (GND). This method is easily interfered by electrical noise. RS485 uses differential signals, which refers to the voltage difference between the A and B lines, which makes RS485’s anti-interference ability very good, far exceeding RS232.
Transmission distance: RS232 is sensitive to noise and its signal mode is limited to short distance (15 meters). RS485 supports long distance transmission up to 1200 meters thanks to the differential signal mode.
Data transmission rate: RS232 is relatively low, with a typical upper limit of around 115.2 kbps. The faster the rate, the shorter the reliable transmission distance. RS485 can support a speed of 10Mbps, but the longer the distance, the lower the maximum rate that can be achieved.
Number of connected devices: RS232 can only connect to 1 device, RS485 can connect to up to 32 load devices.
Connect a few wires: RS232 requires a ground wire, a send wire, a receive wire, and some signal wires. RS485 usually only requires two wires, A and B.
Cost: RS232 is cheap, and the wiring is straightforward if it is just one device connected to another. RS485 is more expensive, and each device requires a dedicated RS485 transceiver chip, which adds a little bit to the device cost.
How to choose RS232 or RS485
For the following application scenarios and requirements, you can choose RS232.
If you only need to connect two devices that are very close to each other, such as in the same control cabinet.
If only one device needs to connect to another device, there is no need for multiple devices to share the line.
If the equipment operates in a clean environment without major electromagnetic interference.
If your application requires two devices to send and receive data simultaneously and independently.
Many traditional devices (such as some old printers, modems) or configuration and debugging ports of many devices.
For the following application scenarios and requirements, you can choose RS485.
If the devices are distributed over a wide area, a communication distance of tens of meters or even thousands of meters is required.
If you need to connect multiple devices (such as multiple sensors, actuators, controllers) to the same communication line.
In factory workshops, outdoors or anywhere there is strong electromagnetic interference.
There are certain requirements for speed (especially over long distances).
Practical implementation & considerations
Once you have chosen the appropriate communication mode, here are the actual hands-on connection and usage suggestions.
The most common RS232 connectors are DB9 and DB25, and their pin numbers are very important (for example, on a computer’s DB9 port, usually 2 is RXD, 3 is TXD, and 5 is GND).
RS485 requires all devices to be connected in parallel to this pair of wires (A and B). In harsh conditions, it is recommended to connect a signal ground wire.
If RS485 is not handled correctly, the signal will be reflected back like an echo, interfering with normal communication, especially at high speeds or long lines. We recommend connecting a 120 ohm terminal resistor in parallel at both physical ends of the RS485 bus to eliminate this reflection.
If your device only has an RS232 interface, you can connect it to an RS485 device via an interface converter.
Conclusion
RS485 can transmit much farther, can connect multiple devices to form a network, and has strong anti-interference ability. The interface you ultimately choose is not about which technology is more advanced, but which one can better meet the actual needs of your project.
