Lithium batteries are everywhere, but do you know what they are? This article will take you through different types of lithium batteries, reveal how cathode materials affect performance, master lithium battery safety knowledge, look forward to the future of lithium batteries, and answer questions about electric vehicle spontaneous combustion.
Last updated: May 2025 | Estimated reading time: 8 minutes
Table of Contents
ToggleQuickly identify different types of lithium batteries

Lithium batteries have become an integral part of modern society, powering a wide range of devices we use every day, from smartphones to electric cars. The lithium battery family includes a variety of types, with the main difference being the electrode material. Common lithium battery types include:
- Lithium-ion battery (Li-ion): This is a rechargeable battery that stores energy by the movement of lithium ions between positive and negative electrodes. Lithium-ion batteries have advantages such as high energy density, high energy efficiency, longer cycle life and longer calendar life.
- Lithium polymer battery: This battery uses polymer gel as electrolyte and is mainly used in handheld electronic devices and has high energy density.
- Lithium Metal Battery: This is a non-rechargeable battery that uses lithium as the negative electrode.
- Lithium Iron Phosphate Batteries: LFP batteries are gaining popularity due to their affordability, high safety standards, low toxicity, and long cycle life. They are widely used in electric vehicles, energy storage systems, and backup power.
Positive electrode materials determine performance differences
The positive electrode material of lithium-ion batteries plays a decisive role in the performance of the battery. Common positive electrode materials include:
- Lithium Cobalt Oxide: LCO batteries have high energy density and are mainly used in portable electronic devices. Our lithium polymer batteries are mainly lithium cobalt oxide batteries, you can click to view our products.
- Nickel-manganese-cobalt: NMC batteries have both energy density, power density and stability and are widely used in electric vehicles. This is one of CATL’s main technology routes.
- Nickel-cobalt-aluminum: NCA batteries have high energy density and are commonly used in high-performance electric vehicles.
- Lithium iron phosphate: LFP battery has excellent thermal stability and safety, mainly in 12V, 24V, 36V, 48V battery pack modules, suitable for energy storage systems and lithium-to-lead-acid projects, check out our lifepo4 battery pack products.
Lithium battery safety knowledge
Improper use of lithium batteries may cause safety hazards. In order to use lithium batteries safely, please pay attention to the following points:
Use and storage:
- Handle lithium batteries with care and do not drop, modify or tamper with the batteries.
- Inspect the battery for signs of damage such as swelling, dents, tears, etc.
- Avoid charging in an overly hot or cold environment. When charging, do it at room temperature and ensure that the surrounding environment is well ventilated.
- Do not keep the battery at 100% charge for a long time.
- When not in use for a long time, charge the battery to about 50% and store it in a cool and dry place.
Charge:
- Use the original charger or one approved by the manufacturer.
- Do not overcharge or leave charging unattended.
- When charging, place the battery on a non-flammable surface.
Prohibited:
- Avoid crushing, puncturing or disassembling the battery.
- Avoid exposing the battery to extreme temperatures.
- Avoid placing the battery together with metal objects to prevent short circuit.
Handle:
- Do not throw lithium batteries into the trash, but take them to a recycling point.
- If the battery has an odor, changes color, overheats, deforms, leaks, or makes unusual noises, stop using it immediately.
The future of lithium batteries
The future of lithium battery technology is promising. Future development trends include:
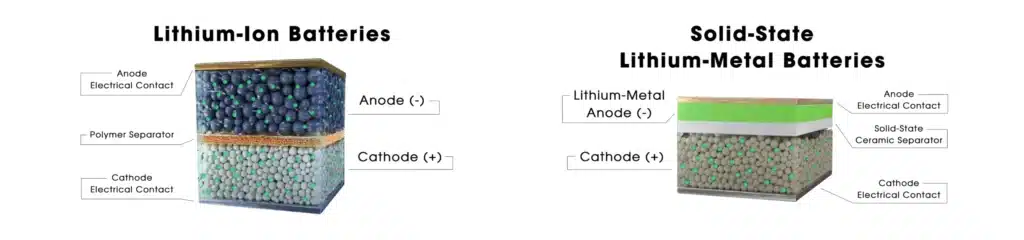
Energy density improvement: By introducing lithium metal anode, energy density is expected to increase by 30-50%.
Solid-state batteries: Solid-state batteries replace the liquid electrolyte of traditional lithium-ion batteries with solid materials, which is expected to improve safety.
New materials: New battery materials such as sodium-ion batteries and graphene batteries are under development, which are expected to provide more sustainable and efficient energy storage solutions.
Recycling technology: As lithium batteries are increasingly used, battery recycling technology is gaining more and more attention. More efficient and environmentally friendly recycling methods will help reduce environmental pollution and achieve resource recycling. View more sustainable lithium battery processing and recycling information.
Why do electric cars sometimes catch fire?
Spontaneous combustion of electric vehicles has become a focus of public attention. Thermal runaway of lithium batteries is the main cause of spontaneous combustion of electric vehicles. Thermal runaway refers to the rapid and uncontrolled increase in temperature and pressure inside the battery, which eventually causes the battery to catch fire or explode.
Factors that can cause thermal runaway include:
External damage: Physical impact, puncture or crushing can damage the internal structure of the battery, causing short circuit or leakage.
Manufacturing defects: Lax quality control, design flaws, or improper assembly may result in batteries with internal defects that could affect safety.
Battery Misuse: Charging or discharging the battery beyond its specified limits may damage the battery.
Extreme Temperatures: Prolonged exposure to high or low temperatures can damage the battery.
Improper Storage: Storing batteries in extreme temperatures, humidity, or near metal objects may cause battery degradation or short circuit.
Are lithium batteries really green energy?
Lithium batteries play a key role in the green energy transition. They can store energy from renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power, thereby reducing dependence on fossil fuels. However, lithium batteries are not completely environmentally friendly. The mining and processing of battery materials such as lithium, cobalt and nickel have a negative impact on the environment and local communities. In addition, the recycling and treatment of waste lithium batteries is also a challenge.
Therefore, we need to continue to innovate, adopt more sustainable materials and processes, and increase battery recycling rates to truly realize the green value of lithium batteries.
Conclusion
Lithium batteries are an indispensable energy carrier in modern society, but they also have certain safety and environmental risks. Only by deeply understanding the characteristics of lithium batteries and mastering safe use methods, our Hongyitai factory actively develops new battery technologies and recycling processes, can we give full play to the advantages of lithium batteries and contribute to building a sustainable future.
