A punctured lithium-ion battery may cause serious safety accidents such as fire and explosion, but the specific reaction depends on the battery type and status. Ternary lithium batteries have the highest puncture risk, while lithium iron phosphate batteries are relatively safe. This article comprehensively analyzes the puncture reactions, key influencing factors and safe handling methods of different types of lithium batteries to help you correctly deal with lithium battery puncture incidents and reduce safety hazards.
Last updated: May 2025 | Estimated reading time: 8 minutes
This article will answer your questions:
- The difference in the reaction of ternary lithium batteries and lithium iron phosphate batteries after puncture.
- What factors determine the degree of danger after a lithium battery is punctured.
- How to safely handle accidentally punctured lithium-ion batteries.
- The latest progress in electric vehicle battery safety standards.
- How to prevent lithium battery puncture accidents.
Table of Contents
ToggleComparison of puncture reactions of different types of lithium batteries
Lithium-ion batteries react very differently after being punctured. Ternary lithium batteries are almost certain to catch fire and explode, while lithium iron phosphate batteries are relatively stable. This difference mainly stems from the chemical material composition and internal structure design of the two batteries, which is directly related to the safety of our daily electronic devices and electric vehicles.
NCM/NCA batteries are widely used in mobile phones, laptops and high-end electric vehicles due to their high energy density, but their safety is their biggest shortcoming. Experiments have shown that when a charged ternary lithium battery is punctured, it will instantly produce an open flame and spread rapidly, releasing a large amount of white smoke, and the fire is extremely difficult to control. The thermal runaway temperature of this type of battery is only about 250°C, and once an internal short circuit occurs, it is easy to trigger a chain reaction.

Safety advantages of lithium iron phosphate batteries:
Lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries perform well in puncture tests, rarely catching fire or exploding even when fully charged. The thermal runaway temperature of these batteries is as high as 800°C, providing greater safety.
| Battery Type | Puncture Reaction | Thermal Runaway Temperature | Practical Implications for You |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ternary Lithium Battery | Immediate ignition, intense fire | ~250°C | High risk of damage to portable devices like phones and laptops |
| Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery | May emit smoke, rarely ignites | ~800°C | Safer for electric bicycles and home energy storage systems |
| Blade Battery (Lithium Iron Phosphate) | Basically no reaction | >800°C | Higher safety for electric vehicles in collisions |
Blade battery technology breakthrough
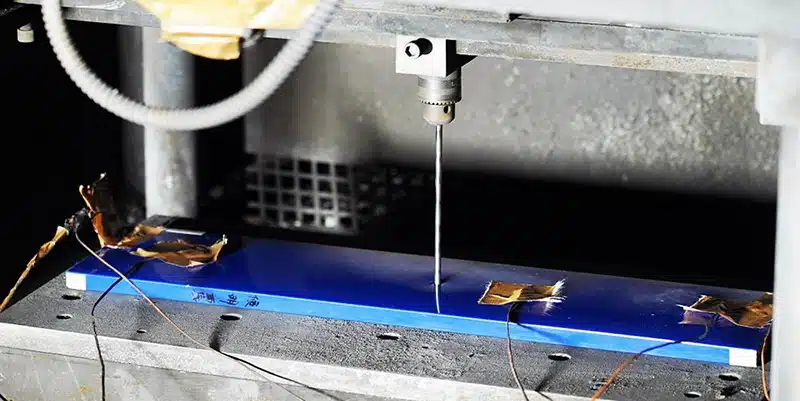
The blade battery developed by BYD uses lithium iron phosphate material and innovatively uses a laminated structure instead of a traditional winding structure, further improving safety. In the needle puncture test, the blade battery had almost no obvious reaction, and the maximum temperature did not exceed 60°C, which is far below the ignition point. This has significantly improved the safety performance of electric vehicles.
An independent test in 2023 showed that an electric vehicle using blade battery technology did not catch fire after a 60km/h collision at the bottom that caused the battery pack to be punctured, while a control model using a ternary lithium battery caught fire under the same conditions and spread to the entire body within 10 minutes.
Key factors affecting battery puncture safety
The degree of danger after a lithium battery puncture depends mainly on four factors: battery charge state, battery type, puncture location and environmental conditions. Understanding how these factors affect each other can help you better assess the risk and take appropriate safety measures.
Battery power status
Battery power is the most important factor affecting puncture safety. Experiments have shown that completely depleted lithium batteries (including ternary lithium batteries) will basically not catch fire or explode when punctured, while puncturing a fully charged battery of the same type will almost certainly lead to a serious accident.
- Fully charged (>80% capacity): The risk of puncture is the highest, and the electrochemical energy stored inside is sufficient to support a sustained thermal runaway reaction.
- Medium charge (30%-80%): The risk is higher, but the reaction may not be as violent as the fully charged state.
- Low charge (<30%): The risk is significantly reduced, but the ternary lithium battery may still react.
- Completely uncharged: The risk is the lowest, and there is basically no open fire or explosion.
This explains why used batteries need to be fully discharged before recycling, and why lithium batteries are usually shipped with a charge level of no more than 30%.

Battery physical state and structural integrity
Batteries that have bulged have a higher risk of puncture than normal batteries. Batteries that have bulged mean that gas has been generated inside and the battery structure and chemical stability have been damaged.
Practical tips and suggestions for users:
- If you find a bulging battery: Stop using the device immediately and do not try to puncture it to vent it.
- Battery appearance deformation: Even if there is no obvious bulge, any deformation may increase the risk of puncture.
- Battery overheating: Abnormal heating of the device may be a precursor to battery problems and should be checked in time.
A report by an electronics manufacturer in 2024 showed that 90% of consumer electronics lithium battery fires were related to previous battery bulging or physical damage, of which 47% of users had tried to continue using swollen batteries by puncturing them to “vent”, which greatly increased safety risks.
Battery safety standards and test methods
Lithium-ion batteries must pass rigorous safety tests to gain market access, and the needle penetration test is one of the key methods for evaluating battery safety performance. Global battery safety standards will become stricter in 2025, requiring manufacturers to provide safer products, which is directly related to the safety of the electronic devices and electric vehicles you use.
Analysis of the latest battery safety standards
China GB 38031 Safety Requirements for Power Batteries for Electric Vehicles is one of the most stringent battery safety standards in the world. The new version will be implemented on July 1, 2026. The core changes of this standard include:
- The thermal runaway requirement has been raised from “no fire or explosion within 5 minutes” to “no fire or explosion”.
- The observation period has been extended from 30 minutes to 2 hours.
- A new bottom impact test has been added to simulate the situation where the battery pack at the bottom of the vehicle is pierced by foreign objects.
- It is required that a warning signal must be provided when a thermal event occurs in the battery.
This means that electric vehicles produced after July 2026 will have greater safety, especially in preventing fire accidents caused by battery puncture.
| Test Item | Old Standard Requirement | New Standard Requirement | Safety Implications for You |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal Runaway Test | No fire or explosion within 5 minutes | No fire or explosion | Significantly reduced risk of vehicle fire |
| Bottom Impact | Not included | 150J energy impact three times without fire | Reduced risk of road debris puncturing the battery |
| External Short Circuit | Basic test | 300 fast charge cycles followed by testing | Increased safety of aging batteries |
Comparison of International Safety Testing Standards
Different countries and regions have different focuses on testing standards for lithium battery safety:
- UN 38.3: Safety standard for lithium batteries in international air transport, including tests such as altitude simulation, temperature cycling, vibration, and shock.
- IEC 62133: Global safety standard for lithium-ion batteries in portable devices.
- UL 1642: Safety standard for lithium battery cells in North America.
- GB 31241: Safety standard for lithium-ion batteries in portable electronic products in China.
Understanding these standards can help you give priority to products that meet strict safety standards when purchasing electronic devices and electric vehicles, thereby reducing the risks of use.
To learn more about battery safety certification, please refer to our battery certification information.
General consumer guide to battery safety
For ordinary consumers, properly handling accidentally punctured lithium batteries is key to avoiding fire and personal injury. The following are detailed emergency handling steps and precautions to help you make the right decisions when facing lithium battery damage.
Emergency treatment for accidental puncture of lithium battery
If your device’s battery is accidentally punctured, follow these steps immediately:
- Immediately move away: Place the device on a non-flammable surface (such as tile, concrete).
- Do not contact liquids: The electrolyte leaked from the battery is toxic and corrosive.
- Observe the reaction: If it starts to smoke or heat up, immediately move to a ventilated place outdoors.
- Prepare to extinguish the fire: Prepare a Class D (metal fire) fire extinguisher. Ordinary water cannot extinguish a lithium battery fire.
- If a fire occurs: Use a large amount of sand to cover the fire or a special fire extinguisher to extinguish the fire. Never use water.
Steps for safe disposal of a punctured lithium battery:
- Place the battery in a fireproof container (such as a metal can).
- Completely cover the battery with sand.
- Contact your local hazardous waste recycling center; do not throw it directly into the regular trash.
- Inform the recycling center that the battery has been punctured so they can take special handling measures.

Precautions in daily use:
The best way to prevent lithium battery puncture accidents is to take preventive measures:
- Avoid physical damage: Do not allow sharp objects to come into contact with the battery or the device containing the battery.
- Prevent overheating: Do not expose the device to high temperatures for long periods of time (such as in a car under direct sunlight).
- Check regularly: Check the device battery once a month for signs of swelling or deformation.
Use original batteries: - Avoid using inferior substitutes or “high-capacity” non-original batteries.
- Beware of swollen batteries: Stop using the battery immediately if you find it swollen, and do not try to puncture it to “vent”.
In March 2024, a user of a certain brand of laptop computer found that the battery was slightly swollen and tried to puncture it with a needle to “vent it”. As a result, the battery caught fire, burning the entire laptop and causing a small room fire. Experts pointed out that chemical changes have occurred inside the swollen battery, and puncturing it will only allow oxygen to enter and accelerate the reaction.
An electric car owner's guide to battery safety
As an electric vehicle owner, it is important to understand the risks of battery puncture and what to do, especially considering that the battery capacity of an electric vehicle is much larger than that of a portable device. The following guide will help you improve electric vehicle battery safety and properly respond to emergencies.
The key to safe maintenance of electric vehicle batteries is to prevent physical damage and standardize use:
- Avoid driving low-floor vehicles on rough roads: Prevent the bottom battery from being punctured by obstacles on the road.
- Check chassis protection regularly: Make sure the battery protection plate is intact.
- Check after a collision: Check the battery status after any collision, even if it is minor.
- Avoid extreme charging: Try to keep the battery charge between 20%-80% in daily use to extend battery life.
- Pay attention to warning signals: Stop and check immediately when the vehicle issues a battery failure warning.
If you are involved in an accident with your electric vehicle and suspect the battery may be punctured:
- Stop the vehicle immediately and turn off the power: Press the emergency stop button or turn off the main power.
- Evacuate the vehicle: Make sure all passengers leave the vehicle and keep a safe distance (at least 15 meters).
- Call professional rescue: Contact a professional rescue team and clearly state that the electric vehicle battery may be damaged.
- Do not extinguish the fire yourself: Lithium-ion battery fires require professional fire-fighting equipment and knowledge.
- Record the incident: Record the accident in detail for insurance and repair needs.
Safety tips for choosing an electric car:
- Prioritize models with lithium iron phosphate batteries: especially products with advanced safety technologies such as blade batteries.
- Check chassis design: evaluate the location and protection of the battery pack.
- Understand the battery warranty policy: including the process of handling battery damage.
- Check battery safety certification: give priority to models that have passed strict safety standard tests.
For more information on electric vehicle battery safety, please refer to the complete guide to electric vehicle battery safety.
Future development trend of battery safety technology
Lithium battery safety technology is undergoing rapid innovation in 2025. From battery materials to structural design, multiple innovations are reshaping battery safety standards. These developments will directly affect the safety performance of electronic devices and electric vehicles you will use in the future, so it is worth paying attention to.
- Solid-state battery technology: Replace liquid electrolytes with solid electrolytes to fundamentally eliminate the risks of leakage and puncture fire.
- Self-healing diaphragm: When the diaphragm inside the battery is damaged, it can automatically repair tiny punctures to prevent short circuits.
- Flame retardant electrolyte: New additives can significantly improve the flame retardant properties of electrolytes.
- Intelligent battery management system: Use AI technology to monitor battery status in real time and provide early warning of potential problems.
Data from China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology in 2025 showed that lithium battery products using new safety technologies have an average 300% improvement in safety performance in puncture tests. This improvement will directly benefit consumers.
Particularly worth mentioning is the “all-round ceramicization” technology, which applies nano-ceramic coatings to key components inside the battery, greatly improving the stability of the battery under extreme conditions. Experiments have shown that even if a battery using this technology is completely punctured, the risk of fire can be reduced by more than 90%.

Market trends and consumer influence:
- Safety becomes a key selling point: Battery safety performance is surpassing energy density to become a key selling point of products.
- Price premium reduction: As the cost of safety technology decreases, the price premium of high-safety battery products gradually decreases.
- Increased consumer awareness: 91% of consumers begin to pay attention to the battery safety performance of electronic products.
- Insurance policy changes: Insurance companies begin to adjust electric vehicle insurance rates based on battery safety technology.
Conclusion
Lithium-ion battery punctures can cause serious safety accidents, but the reactions of different types of batteries vary greatly. Ternary lithium batteries are the most dangerous when punctured, while lithium iron phosphate batteries (especially blade batteries) have better safety performance. The battery’s charge state is the most critical factor in determining the risk of puncture. A completely discharged battery is basically safe even if it is punctured.
As global lithium battery safety standards are comprehensively improved in 2025-2026, we have reason to expect that safer battery products will enter the market, but as users, it is still crucial to maintain safety awareness and correct usage habits.
We, Hongyitai, have been focusing on lithium-ion battery production for more than 10 years, providing customized lithium-ion battery solutions for customers in more than 100 countries and regions around the world. All our products have passed international safety certifications such as UN38.3, IEC62133, and UL, and adopt the industry-leading anti-puncture safety design. Click on our official website to learn more.
FAQs
Immediately place on a non-flammable surface away from combustibles. Do not touch the leaking liquid, it is corrosive. If it starts to smoke or heat up, move outside quickly. Contact a professional recycling agency to dispose of the punctured battery, do not throw it into the ordinary trash.
Lithium iron phosphate batteries are significantly safer than ternary lithium batteries. In puncture tests, ternary lithium batteries are almost certain to catch fire and explode, while lithium iron phosphate batteries rarely catch fire even if punctured. The thermal runaway temperature of lithium iron phosphate (800°C) is much higher than that of ternary lithium (250°C), providing users with a greater safety margin.
Batteries that are completely discharged usually do not explode or catch fire when punctured. Tests have shown that even NMC batteries, which are less safe, will not react significantly when punctured when fully discharged. This is why used batteries need to be fully discharged before recycling.
The internal structure of a bulging battery has been damaged, and "degassing" will only allow air to enter the battery and come into contact with sensitive materials, increasing the risk of fire. Bulging means that chemical changes have occurred inside the battery and it cannot be restored to normal function. It must be stopped and properly recycled.
Blade batteries not only use lithium iron phosphate materials, which are relatively safe in themselves, but also innovatively use a laminated structure to replace the traditional winding structure to achieve more uniform current density and better heat dissipation performance. At the same time, the honeycomb structure design it adopts improves physical strength and comprehensively improves the safety of the battery under extreme conditions.
