When the batteries in your mobile phone, electric car or energy storage device are no longer strong, are you curious about what their “death” means? When lithium-ion batteries are scrapped, it is not the end of their life, but they enter another cycle stage. From the factors that affect the life span to the value of recycling, this guide will reveal the secrets of the entire life cycle of lithium batteries.
Last updated: May 2025 | Estimated reading time: 8 minutes

This article will answer your questions:
- How to tell if your lithium battery is “dead” or needs to be replaced
- The actual impact and safety risks of running out of power on lithium batteries
- Emergency measures when electric vehicle batteries are dead
- Seven practical tips to extend the life of lithium batteries
- The hidden economic value and recycling process of used lithium batteries
Table of Contents
ToggleLithium battery life cycle and scrap determination
Lithium batteries do not die suddenly, but experience a gradual performance degradation process. When the battery capacity decays to less than 80% of the original design capacity, it is generally considered to have reached the end of its life, especially in electric vehicle applications. This decay is inevitable, but the speed varies depending on usage habits.
Lithium batteries in consumer electronics products can usually be used for 2-3 years, electric bicycle batteries can be used for 3-5 years, and electric vehicle batteries are designed to have a service life of 8-10 years. Research data shows that the average lithium-ion battery will experience significant capacity decay after 300-500 complete charge and discharge cycles.
Clear signals to determine whether lithium batteries need to be scrapped
When your lithium battery exhibits the following symptoms, it may be nearing the end of its life:
| Failure Signal | Consumer Electronics | Electric Vehicles | Practical Significance for You |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capacity Degradation | Less than 50% of original usage time after full charge | Driving range reduced to below 80% | Need to charge more frequently, affecting normal usage |
| Physical Deformation | Battery swelling, bulging | Battery pack deformation or leaking | Increased safety risk; should stop using immediately |
| Charging Abnormality | Charging time extended by more than 2x | Fast charging function fails or charging abnormally slow | Significantly reduced usage efficiency; daily experience suffers |
| Performance Instability | Battery level display fluctuates wildly | “Turtle mode” activated frequently | Reduced reliability, increased usage anxiety |
- Mobile phone battery capacity drops significantly: Consider replacing the battery instead of the whole device, which can save 60-70% of the cost.
- Electric bicycle battery performance drops: Using a battery activation charger may extend the service life by 3-6 months.
- Electric vehicle power battery retirement: Check the manufacturer’s recycling plan, some brands offer replacement discounts.
Mr. Li, a Tesla Model 3 owner, found that the battery capacity had dropped to 82% after five years of use. An official diagnosis confirmed that the battery was still within the normal range of use, avoiding unnecessary replacement costs.
Effects of power exhaustion on lithium batteries
A completely exhausted lithium battery is not the most dangerous state, but it will accelerate capacity decay. Contrary to popular belief, the risk of spontaneous combustion of a completely exhausted lithium battery is relatively low because the internal chemical reaction is slowed down. However, a deep discharge may shorten the battery cycle life by 5%-8%.
When lithium batteries are not used for a long time, self-discharge will cause the battery power to gradually lose. The monthly self-discharge rate of new batteries is about 3-5%, but as the use time increases, this ratio will gradually increase to 8-10%. Therefore, even if lithium batteries are not used, they should be charged regularly to maintain a power state of 30%-50%.
Safety risk assessment of a completely depleted battery
- Spontaneous combustion risk: A fully depleted battery has a low risk of spontaneous combustion, but overcharging, physical damage, and high temperature environments are the main risk factors.
- Battery activation challenges: When the voltage is less than 2.5V/cell, ordinary chargers cannot safely activate the battery, and professional equipment is required.
- Permanent capacity loss: After full discharge, some active materials may lose their activity irreversibly, permanently affecting the capacity.
When the power of the lithium iron battery drops to about 25%, the voltage will quickly drop to the power-off protection threshold of the battery management system (about 3V/cell), resulting in a sudden power outage. This is a protection measure rather than a fault, and its purpose is to prevent damage caused by excessive discharge of the battery.
Electric vehicle battery dead emergency response guide
When the electric vehicle is close to running out of power, the vehicle will automatically enter “turtle mode” and limit the maximum speed to below 40km/h. This is a protection mechanism of the battery management system, which minimizes energy consumption and helps you reach the nearest charging station safely.
When the battery is completely exhausted, the power system will gradually fail, but it will not stop immediately. At this time, the auxiliary systems (air conditioning and entertainment system) will be turned off first to prioritize the power supply of safety systems such as braking and steering, so that you can find a parking space as soon as possible.

Emergency steps when the battery runs out:
- Identify warning signals: The red warning light on the dashboard lights up, and the range is displayed as “—” or a very low value.
- Reduce speed immediately: Slow down to below 40km/h and avoid sudden acceleration.
- Turn off non-essential power devices: Power-consuming devices such as air conditioners and audio equipment should be turned off immediately.
- Find a safe parking area: Prioritize service areas or charging stations, followed by emergency lanes.
- Contact rescue: Use your mobile phone or the in-vehicle SOS system to contact rescue services.
- Wait for professional help: Ordinary charging piles may not be able to activate a fully discharged battery.
Ms. Zhang from Shanghai’s electric car suddenly ran out of power on the highway. She followed the instructions in the vehicle manual to activate the emergency mode and successfully drove the vehicle into a service area 3 kilometers away, avoiding the dangerous situation of breaking down on the highway.
Practical tips to extend the service life of lithium batteries
Avoiding full charge and discharge is the most effective way to extend the life of lithium batteries. Keeping the battery in the range of 20%-80% can extend the cycle life by 2-3 times. Data shows that lithium batteries that are frequently charged to 100% and fully discharged have a cycle life of only 40%-60% of batteries that are moderately charged and discharged.
Temperature management is also critical. Lithium batteries perform best at around 25°C. When the temperature exceeds 35°C, the battery ages faster, and the battery life may be cut in half for every 10°C increase. Similarly, use below 0°C will cause temporary capacity loss, and frequent low-temperature use may cause permanent damage.
Battery maintenance strategies in different scenarios
| Device Type | Best Charging Habits | Behaviors to Avoid | Storage Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phone/Laptop | Maintain battery between 20%-80% charge | Using while charging, overnight charging | Store in partially charged state, charge once a month |
| Electric Bicycle | Use smart charger, set to 80% charge | Charging immediately after rain | Indoor environment, 20%-50% charge |
| Electric Vehicle | Use timed charging function to 80% | Frequent fast charging, long-term full storage | If unused for extended periods, set charging limit to 60% |
7 tips to extend your life that you can implement right now:
- Control the upper limit of charging: Set the upper limit of charging for mobile phones, laptops and other devices to 80%.
- Avoid extreme temperatures: Avoid charging the device in direct sunlight or using it in a cold environment.
- Use the original charger: The matching charger provides appropriate charging parameters to avoid damage.
- Regular shallow cycle: Electric vehicles perform 20%-80% charge and discharge cycles every week to help maintain battery activity.
- Avoid long-term full charge: Storing lithium batteries at full charge will accelerate aging, and the ideal storage capacity is 40%-60%.
- Regular use: Even devices that are not often used should be charged and discharged once a month.
- Update battery management software: Ensure that the device uses the latest battery management algorithm.
According to CATL’s research, limiting the upper limit of charging to 80% using the vehicle system can extend the expected life of electric vehicle batteries by 20%-30%, equivalent to an additional 2-3 years of use. Read more.
Recycling value and treatment path of waste lithium batteries
An electric car battery contains about 8kg of lithium, 40kg of nickel, 10kg of cobalt and other precious metals. Calculated at 2025 prices, the recycling value is more than 15,000 yuan. With the popularization of electric vehicles, it is expected that 11 million tons of lithium-ion batteries will reach the end of their service life by 2030, and the resources contained in them are of great value.
At present, there are two main paths for lithium battery recycling: secondary utilization and material recycling. Secondary utilization refers to reassembling batteries with a capacity reduced to 80%-20% for use in energy storage and other scenarios with lower performance requirements. Material recycling is to extract valuable metal materials for reuse through physical and chemical treatment.
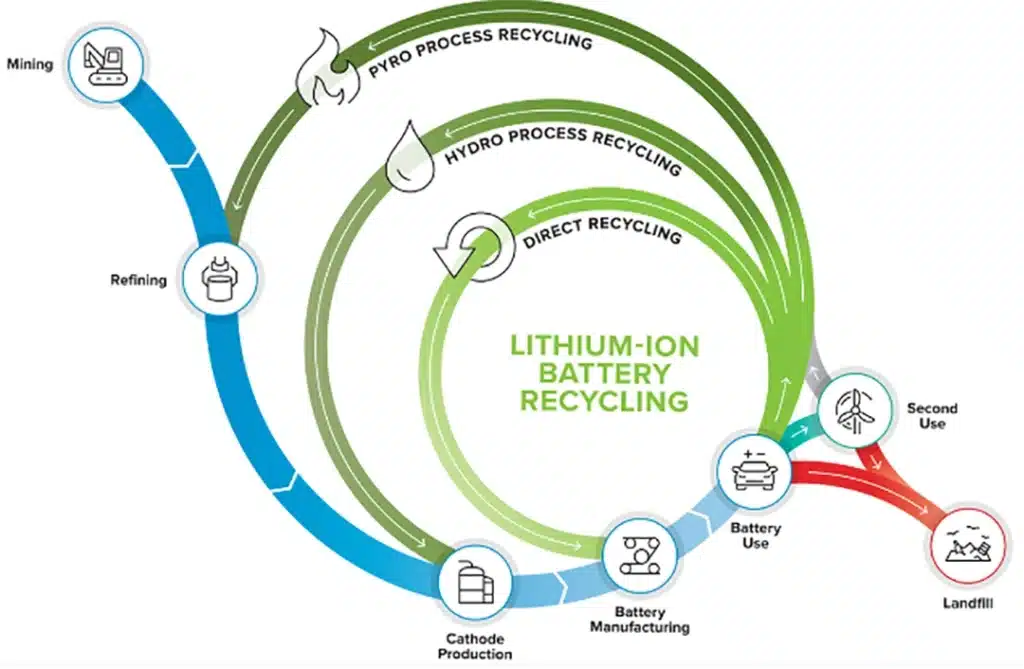
Technical route for lithium battery recycling and treatment
Wet recycling technology can achieve a 99.6% recovery rate for nickel, cobalt, and manganese and a 91% recovery rate for lithium, but the processing cost is relatively high. Fire recycling has lower costs but has a greater environmental impact. With technological advances, recycling costs continue to decline, from 2,000 yuan/ton in 2018 to about 700 yuan/ton in 2025.
Small lithium batteries for ordinary consumers (mobile phones, tablets, etc.) can be recycled through the following channels:
- Manufacturer’s official recycling program: Some electronic product manufacturers provide old battery recycling services, and some also offer discounts.
- Community recycling points: Many cities have special electronic waste recycling points.
- Electric vehicle 4S stores: Most electric vehicle brands provide old battery recycling services.
- Professional recycling companies: Lithium battery recycling companies will provide door-to-door collection services, and some also provide cash recycling.
Estimating the economic value of battery recycling
| Battery Type | Average Recycling Value | Primary Recyclable Materials | Environmental Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phone Battery | 5-10 RMB/unit | Lithium, Cobalt, Copper | Prevents 1kg of harmful substances from entering the environment |
| Electric Bicycle Battery | 100-200 RMB/set | Lithium, Copper, Aluminum | Reduces 5-8kg of carbon emissions |
| Electric Vehicle Battery | 8000-15000 RMB/set | Lithium, Nickel, Cobalt, Manganese, Aluminum | Reduces 60-90kg of carbon emissions |
The latest lithium battery technology development and recycling trends in 2025
In 2025, lithium battery technology has achieved commercial application of solid-state batteries, and the cycle life has increased to more than twice that of traditional lithium batteries. At the same time, battery design is developing in the direction of easier disassembly and recycling. The application of battery passport technology gives each battery a unique “identity card” to facilitate tracking and management throughout its life cycle.
- Solid-state battery commercialization: Solve safety issues while extending life, and reduce waste by about 30%.
- Battery design innovation: Modular design reduces disassembly costs by 40% and increases recycling efficiency by 35%.
- Recycling technology breakthrough: New selective precipitation technology increases lithium recovery rate to more than 95%.
- Global regulations are becoming stricter: The European Union, China, and the United States have all introduced stricter battery recycling regulations, requiring higher recycling rates.
The lithium battery recycling market is growing at an annual rate of 30% and is expected to reach 30 billion yuan in 2026. At the same time, advances in recycling technology have reduced the cost of recycled materials to 70%-80% of virgin materials, significantly improving economic feasibility.
Conclusion
Lithium batteries are not worthless when they “die”, but enter the next stage of their life cycle. By correctly judging the scrapping signals, using and maintaining them scientifically, you can maximize the life of lithium batteries. When the battery finally needs to be replaced, recycling it through formal channels can not only obtain financial compensation, but also contribute to environmental protection.
From now on, set your device’s charge limit to 80%, avoid full discharge, control the ambient temperature, and perform shallow charge and discharge cycles regularly. These simple habits can extend your battery life by at least 30%. For scrapped batteries, remember to contact official recycling channels or professional recycling companies to maximize the use of resources.
We at Hongyitai have been focusing on lithium-ion battery production for more than 10 years and have provided customized lithium-ion battery solutions to customers in more than 100 countries and regions around the world. With ISO9001/14001 certified factories and strict quality management systems, we ensure that each battery meets international safety standards. To learn more about lithium battery solutions, click here to contact us.
FAQs
Undisassembled lithium batteries are not hazardous waste, but they are resource-based waste that should be recycled. Some components of disassembled batteries (such as electrolyte) may be hazardous waste. Ordinary consumers should put waste batteries into special recycling bins instead of mixing them with household garbage.
Power banks are lithium battery products, so the positive and negative electrodes should be sealed with tape, put into a plastic bag and sealed, and then sent to an electronic product recycling point or a hazardous waste recycling point. Many electronic product retailers also provide recycling services, such as Apple, Xiaomi and other brand stores.
Modern electric vehicle batteries are designed to have a lifespan of 8-10 years or 160,000-200,000 kilometers. In actual use, electric vehicle batteries produced in 2025 can still maintain more than 80% of their capacity after 10 years under normal use conditions.
